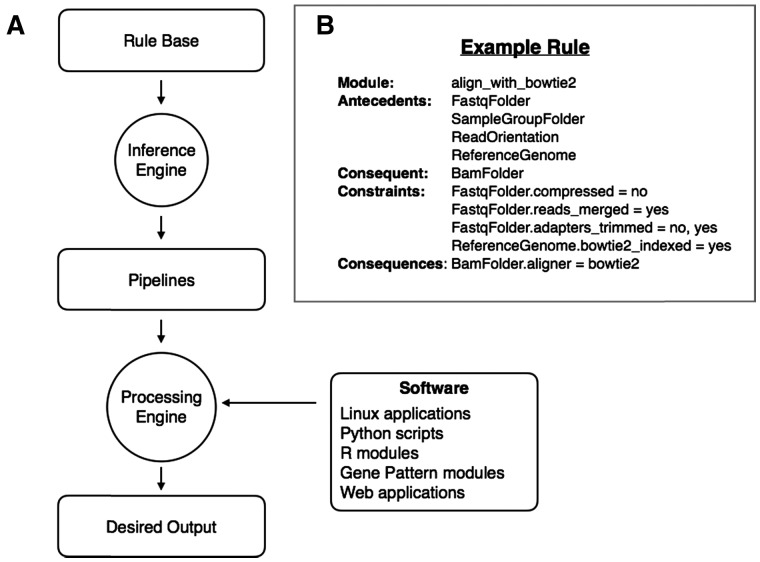
Fig. 1.
BETSY Architecture. (A) The BETSY knowledge base system consists of a Rule Base that describes (1) the types of data encountered in bioinformatics, and (2) the ability of bioinformatics software to transform data from one type to another. Given these components, the Inference Engine uses a backwards-chaining algorithm to produce a pipeline that describes how to generate a target object of interest, given the inputs available. Then, the Processing Engine can run the pipeline to produce the output requested. (B) This shows the structure of an example rule from the knowledge base. This rule describes a module that aligns next generation sequencing reads using the Bowtie2 algorithm. It requires a set of antecedents including a folder of the FASTQ format files to be aligned, a mapping of the files to samples, a description of the orientation of the reads, as well as the reference genome. Given these inputs, the module produces a folder of BAM files. The Constraints set the conditions on the antecedents that must exist before this rule can be applied. For instance, the FASTQ files cannot be compressed. However, the adapters may or may not be trimmed. The Consequences describe the changes that are imposed on the consequent after this module is run. Here, the aligner attribute for the BAM files is set to bowtie2