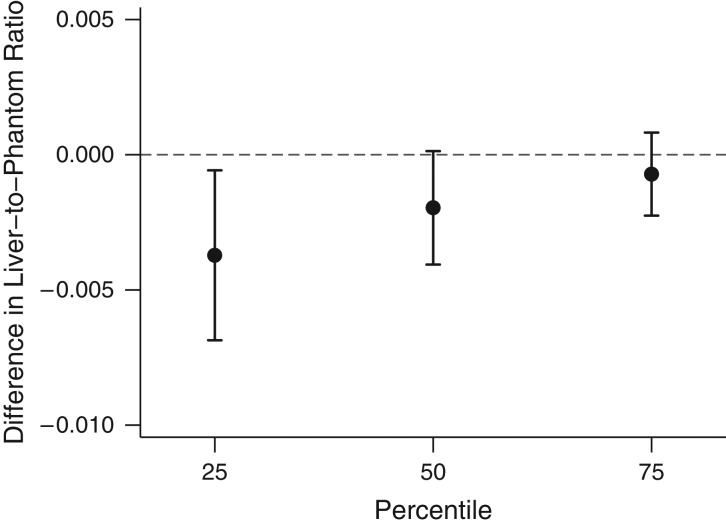
Figure 2.
Associations between distance to the nearest major roadway and the 25th, 50th, and 75th percentiles of the distribution of liver-to-phantom ratio in participants from the Multi-Detector Computed Tomography Study, Boston, Massachusetts, 2002–2005. Models adjusted for age at MDCT scan and (age at MDCT scan)2, sex, cigarette-smoking status (current, former, or never), pack-years of smoking, alcohol intake, educational level, usual occupation, physical activity, antihypertensive medication use, statin use, quartile of median household income in the participant's census tract in 2000, median value of owner-occupied housing units in the census tract, population density (population/km2) in the census tract, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and an exam identifier. Results were scaled to approximate comparing participants who lived 58 m from the nearest major roadway with those who lived 416 m from the nearest major roadway. Bars: 95% confidence intervals.