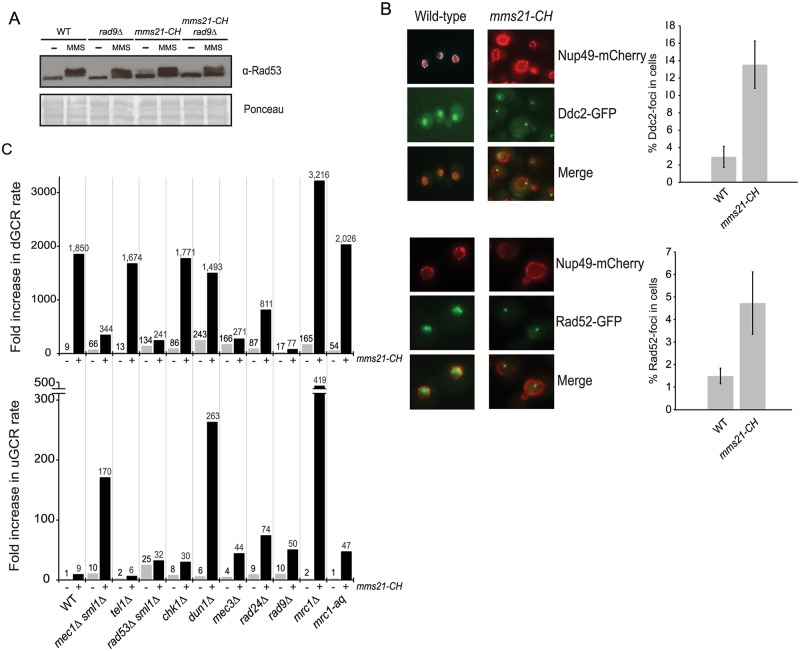
Fig 6. Role of DNA damage checkpoint in the formation of GCRs.
A) Rad53 gel shift assay to examine Rad53 activation in WT, mms21-CH, rad9Δ and rad9Δ mms21-CH mutants. B) Spontaneous Ddc2 foci in mms21-CH mutant and WT, which also contain Nup49-mCherry to mark the nuclear envelope. Bar graph indicates the percentage of Ddc2-foci within the nuclear envelope (marked by Nup49-mCherry). Error bars represent the standard deviation from three replicate experiments using two biological isolates per strain per replicate. 200–400 cells were imaged and counted for each experiment. C) dGCR and uGCR rates caused by mutations of DNA damage checkpoint genes with or without mms21-CH. The number above each bar indicates the fold change normalized to the uGCR rate of wild-type strain. Detailed results used to generate the bar graph are shown in S6 Table.