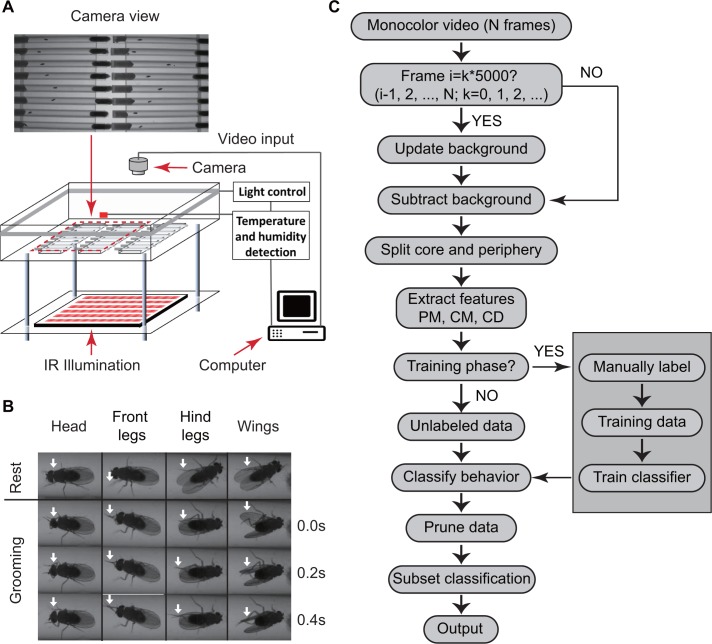
Figure 1. Overview of approach for detecting Drosophila grooming.
(A) Apparatus used in recording behavior. Flies constrained to individual tubes are continuously illuminated by infrared light from below and recorded by a digital camera from above. LED lights on sides of chamber simulate day-night light conditions. Temperature and humidity probes placed in the chamber are monitored by a computer. Inset: Camera photo of fly tubes in chamber. (B) Examples of the most commonly observed types of grooming in our experiments. The top row displays postures of a fly in inactive state. The three rows below show how the limbs and body of a fly coordinate to perform specific grooming movements. Arrows point to the moving part during grooming. (C) Flowchart of our algorithm used to classify fly behavior. After generating a suitable background image, the algorithm characterizes movements of fly center (CD), core (CM) and periphery (PM) to fully classify behavior in each frame.