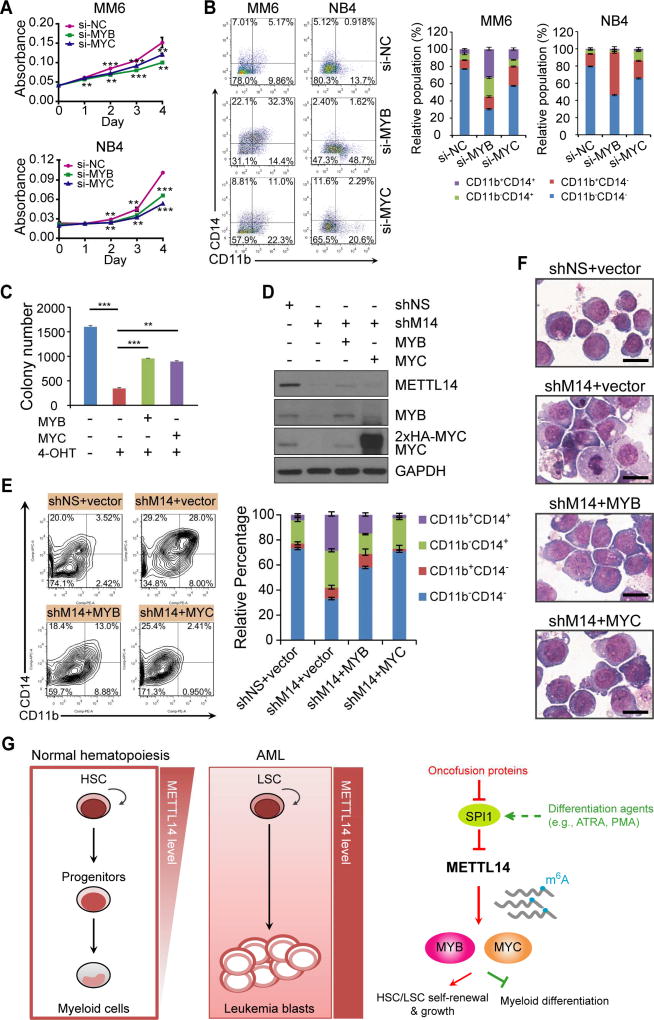
Figure 7. MYB and MYC are critical targets of METTL14 that mediates myeloid differentiation block and AML cell proliferation.
(A, B) Effect of MYB or MYC silencing on cell growth (A) and differentiation (B) of AML cell lines.
(C) BM leukemic cells from the fl/fl-CT primary BMT mice were transduced with pmiRA1 empty vector or MYB or MYC expression vector and seeded for colony-forming assay with or without 4-OHT (1 µM). Colony numbers were counted and compared.
(D) MM6 cells were transduced with shNS or shM14-#2, and with or without MYB or MYC encoding lentivirus as indicated. Western blots showing knockdown of METTL14 as well as ectopic expression of MYB or MYC in the corresponding groups.
(E) MYB or MYC overexpression rescues terminal myeloid differentiation of MM6 cells induced by METTL14 knockdown. Representative images of flow cytometric analysis of CD11b and CD14 staining were shown on left and the mean percentages of each population were shown on right.
(F) Wright-Giemsa staining of MM6 cells showing reduced differentiation in cells with MYB (shM14+MYB) or MYC (shM14+MYC) overexpression as compared to those with empty vector (shM14+vector) when METTL14 was knocked down. Bar= 20 µm.
(G) Proposed model depicting regulation and role of METTL14 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis.
Mean±SD values are shown for Figures 7A and 7C. **, p <0.01; ***, p < 0.001; t-test. See also Figure S7.