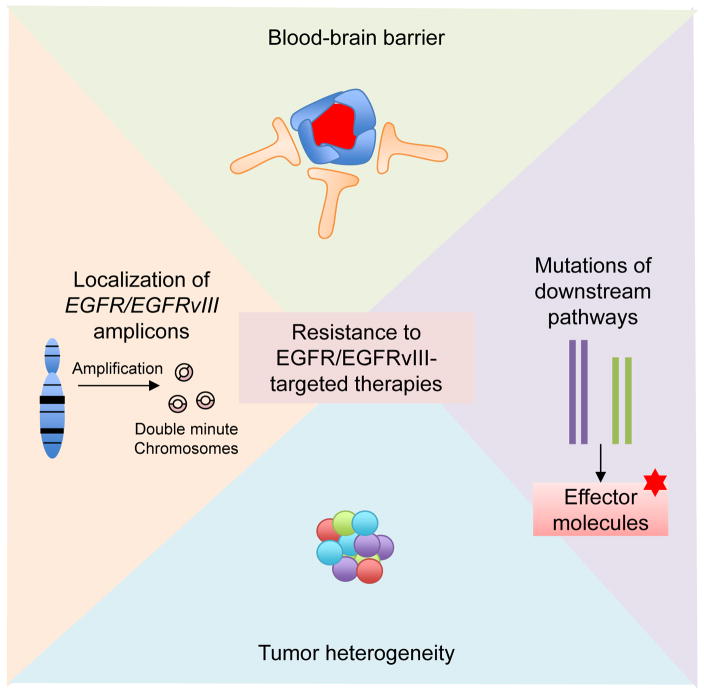
Figure 4. Factors contributing to resistance to EGFR/EGFRvIII-targeted therapies.
Factors contributing to resistance to EGFR/EGFRvIII inhibition include blood-brain barrier penetrance (i.e. many antibodies and chemicals cannot across the blood-brain barrier), mutations of signaling molecules downstream of EGFR/EGFRvIII (i.e. PTEN mutation and NF1 mutation, which maintain activation of downstream pathways despite upstream inhibition), tumor heterogeneity (distinct tumor cells can harbor different mutations or receptor kinase amplification, interaction between tumor cells and stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment) and extrachromosomal localization of EGFR and EGFRvIII amplicons (facilitating the cells’ ability to evade EGFR inhibitors).