Fig. 9. Treatment of EC with MEK inhibitor abrogates mTORC2-mediated over-activation of ERK mediated in response to HLA II antibody.
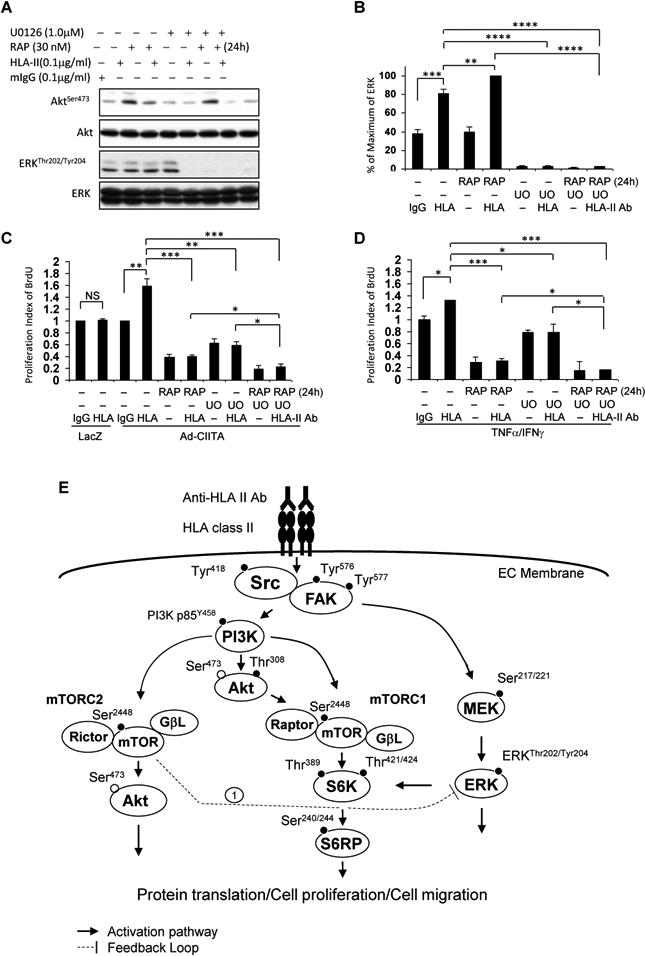
EC were C infected with Ad-LacZ or Ad-CIITA or A, B, D pretreated with TNFα/IFNγ for 48 h. Starved cells were pretreated with 30 nM rapamycin for 24 h and/or 1.0 μM UO126 for 60 min. A, B. Cells were stimulated with 0.1 μg/ml HLA class II antibody for 15 min. Treatment of EC with mIgG serves as negative control. Proteins in the precleared cell lysates were separated by 6∼15% SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting withanti-phospho-Akt Ser473, or ERK1/2 Thr202/Tyr204 antibodies. The membranes were re-probed with anti-Akt or ERK total antibodies to confirm equal loading of proteins. B Phosphorylated protein bands shown in A were quantified by densitometry scan analysis and results are expressed as the mean ± SEM percentage of maximal increase in phosphorylation above control values. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001 were analyzed by one way ANOVA with Fisher's LSD. C, D Cells were stimulated with 1.0 μg/ml HLA class II antibody for 48 h, incorporated with BrdU for 2 h, and harvested. EC proliferation was measured by flow cytometry. DNA synthesis S phase was gated, and proliferation index is presented as fold increase in the percentage of cells positive for BrdU normalized to negative control. The bar graphs show the mean ± SEM fold change of proliferation index. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 were analyzed by one way ANOVA with Fisher's LSD. Data represent at least three independent experiments. E. Scheme representing HLA class II antibody-triggered activation of intracellular signal networks in EC leading to cell proliferation and migration. EC were infected with Ad-CIITA or pretreated with TNFα/IFNγ for 48 h to up-regulate HLA class II molecule expression. Ligation of HLA II molecules with antibody stimulates phosphorylation of protein tyrosine kinases, including Src Tyr418, FAK Tyr576 and Tyr577. Dissecting the upstream/downstream interactions using siRNA and pharmacological inhibitors, weshow that Src is the earliest protein kinase in the HLA II antibody-induced signaling cascade. Activated FAK/Src signaling complex mediates phosphorylation of p85 PI3K Tyr458, Akt Thr308, and Akt Ser473. The PI3K/Akt cascade stimulates phosphorylation of mTOR and assembly of mTORC1 and mTORC2. mTORC1 induces phosphorylation of S6K Thr389 and Thr421/Ser424. mTORC1/S6K signal axis phosphorylates S6RP at Ser240/244. mTORC2 mediates phosphorylation of Akt at Ser473. In parallel to the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal pathways, activated FAK/Src complex also stimulates activation of the MEK/ERK pathway. These signal networks, solid lines, regulate HLA antibody-stimulated cell proliferation and migration. Long-term treatment with rapamycin, everolimus, anactive-site inhibitor or knockdown Rictor with siRNA mediates mTORC2 negatively feedbacks to enhance phosphorylation of ERK (negative feedback loop 1). Solid line with arrow presents stimulatory signal transduction pathways. The dotted line presents negative feedback loop.
