Figure 3. The biological effects of LL-37 citrullination on phagocytes.
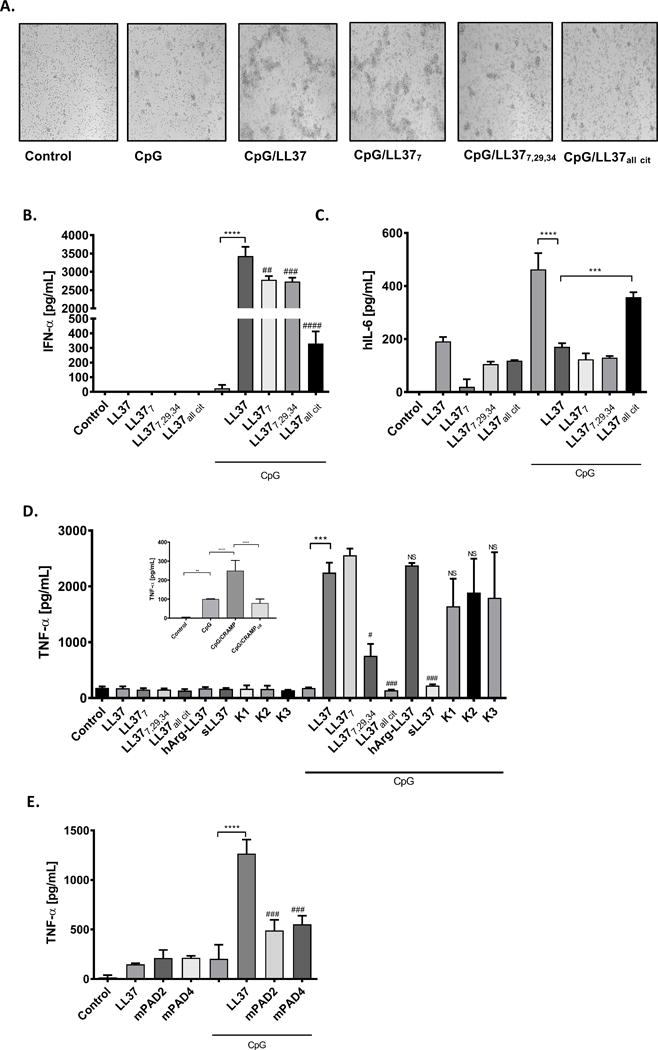
Primary human pDCs or murine macrophages cell line (RAW 264.7) were incubated with CpG (3 mM) or CpG combined with differentially citrullinated LL-37 forms (28.8 mg/mL) for 15 min. Thereafter cells were washed 3 times with PBS and incubated in fresh medium for additional 20 h. (A) Formation of cell clumps reflecting the activation of human pDCs; (B) IFN-α and (C) IL-6 levels measured by ELISA in culture supernatant. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons post-test (***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001- comparing to control; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001, comparing with CpG-LL37). (D) The expression of TNF-α in murine macrophages upon exposition to CpG alone, CpG with human synthetic native and different modified forms of LL-37 or CpG with murine native and citrullinated cathelicidin (CRAMP) – insert. TNF-α secretion to the culture supernatant was measured with ELISA. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons post-test (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001; compared to control; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001, compared with CpG-LL37). (E) Raw 264.7 were stimulated with CpG (10uM) alone or with mixtures of peptides (mPAD2 and mPAD4) that resemble the catalytic modification of LL-37 by PAD2 and PAD4, respectively. TNF-α production in the culture supernatant was measured with ELISA. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons post-test (****P<0.0001 – compared to control; ###P<0.001, compared to CpG-LL37).
