FIGURE 4. VDR activation of anti-microbial peptides appeared to be required for the IL-12+IL-18-mediated growth inhibition of intracellular mycobacteria.
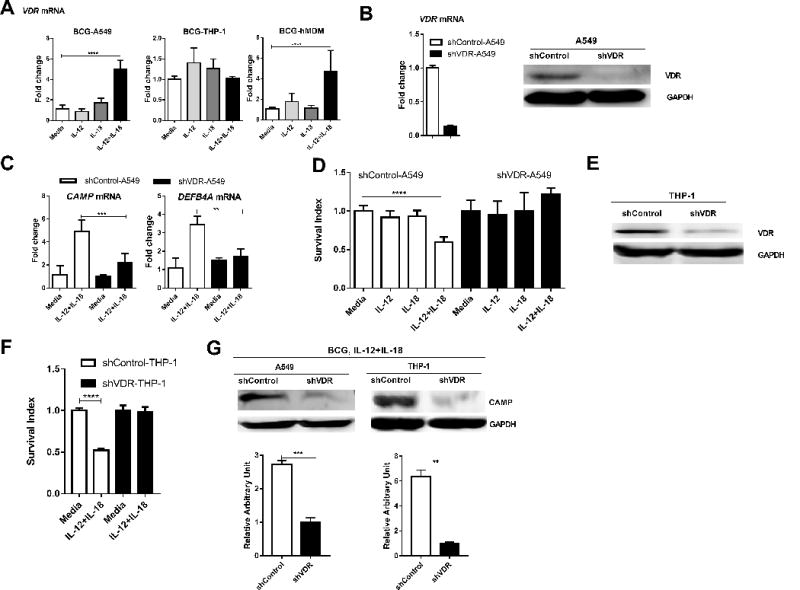
(A) shows mean fold changes in expression levels for VDR in BCG-infected A549, THP-1 cells and hMDM, respectively, in the presence of media, IL-12, IL-18 or IL-12+IL-18. Data are derived from 4 independent experiments using A549 or THP-1 cells, and 3 independent experiments using hMDM from 12 healthy uninfected donors. P values are calculated through ANOVA then Dunnett’s test compared with control condition: treated with culture media, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. (B) shows representative data demonstrating the knock-down for the VDR at both mRNA (left, RT-qPCR) and protein (right, western blot) levels in A549 cells stably transduced with the lentivirus construct LV-shVDR in comparisons with the control. Stably transduced cell lines were selected by 2 ug/ml puromycin treatment of cultures. (C) compares fold changes in expression levels of CAMP and DEFB4A between BCG-infected shVDR- and shControl-transduced A549 cells in the presence of media or IL-12+IL-18 for 24 hours. Data were generated by RT-qPCR, and pooled from three independent experiments. P values are calculated through T test, ** p<0.01, *** p < 0.001. (D) shows changes in mean Survival indexes for BCG bacilli in BCG-infected shVDR- and shControl-transduced A549 cells in the presence of media, IL-12, IL-18 or IL-12+IL-18. Data are derived from four independent experiments. Note that VDR knock-down led to reversion of IL-12+IL-18-mediated inhibition of BCG growth. P values are calculated through ANOVA then Dunnett’s test compared with control condition: treated with culture media, **** p < 0.0001. (E) shows representative western blot data demonstrating the VDR knock-down in THP-1 cells in comparisons with the shRNA control. (F) Bar graph shows that shRNA knock-down of VDR reverses the growth restriction of intracellular mycobacteria during IL-12+IL-18 treatment of BCG-infected THP-1 cells when compared with shRNA control. Data are derived from 8 replicates in 2 independent experiments. P values are calculated through T test, **** p< 0.0001. (G) Representative western blot analysis shows that shRNA knock-down of VDR abrogated the ability of the IL-12+IL-18 treatment to induce the CAMP expression in BCG-infected A549 and -THP-1 cells, respectively. The upper panel are representative western blot analysis from 4 replicates, the lower panel are quantitative analysis of CAMP protein levels by densitometry. P values are calculated through T test compared with control condition: treated with culture media, ** p< 0.01, *** p< 0.001.
