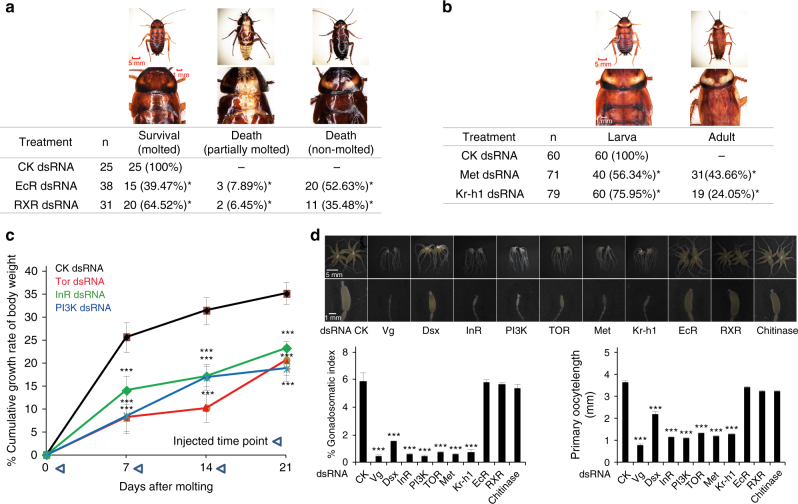
Fig. 4.
Functional studies of pathways regulating development and reproduction in the American cockroach. a Regulation of molting by ecdysone receptor (EcR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) genes in the 20E signal pathway. Mortality rates were checked after RNAi treatment of indicated numbers of individuals (n). CK, control dsRNA corresponds to that in Fig. 3. b Regulation of metamorphosis by methoprene-tolerant (Met) and kruppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1) in the juvenile hormone (JH) pathway. Adult proportion index was checked after the JH singling was disrupted. c Regulation of growth by the insulin signaling pathway genes. Insulin-like receptor (InR), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and target of rapamycin (TOR) genes were repeatedly depleted by dsRNA injection during 3 weeks. Three injections were given and cumulative growth rate of body weight (%) was calculated. Student’s t-test: ***p < 0.001. d Morphology change of ovary maturation during the first reproductive cycle in virgin females. Vitellogenin (Vg), double-sex (Dsx), and nine genes involved in the pathways of insulin, JH, and 20E were knocked down by RNAi. Gonadosomatic index and primary oocyte length were used to evaluate the ovary maturation degree. All the data were calculated as the mean value of three replicates. Error bars represent standard deviation. Two-tailed Student’s t-test: *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. Details of all involved pathways are shown in Supplementary Tables 16–18