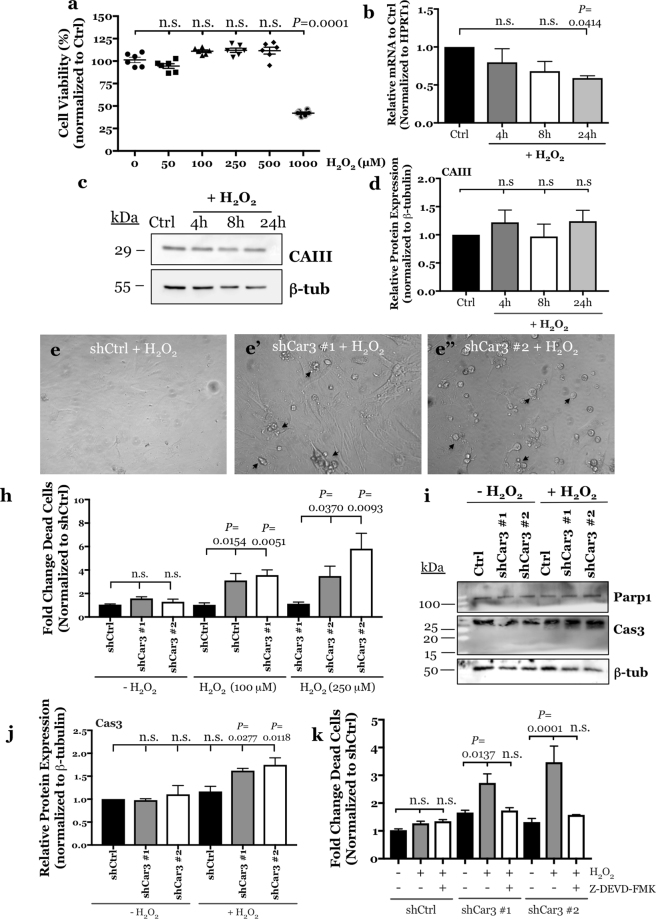
Figure 5.
CAIII protects NP cells from oxidative stress-induced, caspase 3-mediated cell death. (a) Rat NP cells are resistant to H2O2-mediated cell death and maintain their viability following treatment with up to 500 μM H2O2. Viability significantly decreases at 1 mM. (b–d) Treatment of rat NP cells with 100 μM H2O2 for 24 hours had no effect on Car3 mRNA expression analysed by qRT-PCR (b) or CAIII protein levels measured by Western blot and subsequent densitometric analyses (c,d). (e) Representative images showing morphology of NP cells transduced with a control shRNA (e) and two independent Car3 shRNAs (e’,e”) and treated with 100 μM H2O2 for 24 hours. CAIII silenced cultures showed increased number of dying cells (marked by black arrows). (h) CAIII silenced NP cells treated with 100 and 250 μM H2O2 for 24 hours showed a significant increase in the fold change of dead cells as compared to control populations. (i) Representative Western blot images of two markers of apoptosis, total and cleaved Parp1 and Cas3. (j) Densitometric analysis of Cas3 protein expression from the Western blot shown in (i) shows that total Cas3 expression is significantly increased in CAIII silenced NP cells after treatment with 100 μM H2O2 for 24 hours. (k) Pre-treatment of CAIII silenced NP cells with Cas3 inhibitor, Z-DEVD-FMK blocked H2O2-induced apoptosis. All quantitative data is represented as mean ± SE, n = 3 independent experiments; 4 technical replicates per experiment were performed when applicable. Oneway ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test was used to determine statistical significance. Ordinary twoway ANOVA used to determine statistical significance in Fig. 5k. n.s, non-significant.