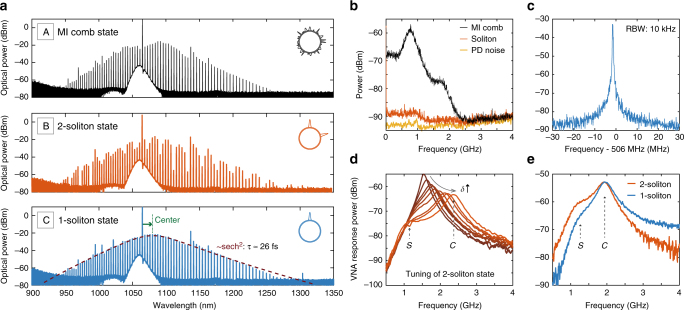
Fig. 2.
Dissipative Kerr solitons at 1 μm and their characterisation. a Optical spectra of the modulation-instability (MI) comb state (A) and two soliton states (B and C) obtained in a 1-THz Si3N4 microresonator (pump is located at around 1065 nm). The transition from two-soliton state (B) to single-soliton state (C) was obtained by backward tuning technique of the pump laser. Insets show the estimated positions of the DKS in corresponding states. The single-soliton state was fitted with the sech2 envelope (dashed dark blue) for an estimated duration of 26 fs. The green arrow shows the Raman-induced red spectral shift of the soliton spectrum with respect to the pump line. b Intensity noise of MI comb state (black), soliton states (red) shown in Fig. 1 a and the noise floor of the photodiode (PD) used for measurements (yellow). c Heterodyne beatnote of the soliton comb line around 1050 nm with a second CW laser. d System response evolution in the two-soliton state shown in a, when increasing the pump-cavity detuning (δ). The positions of characteristic -resonance and -resonance are indicated with C and S letters correspondingly. e System response evolution when the DKS state is switched from two-soliton to single-soliton state. The amplitude of the -resonance has decreased, because the number of intracavity solitons is reduced