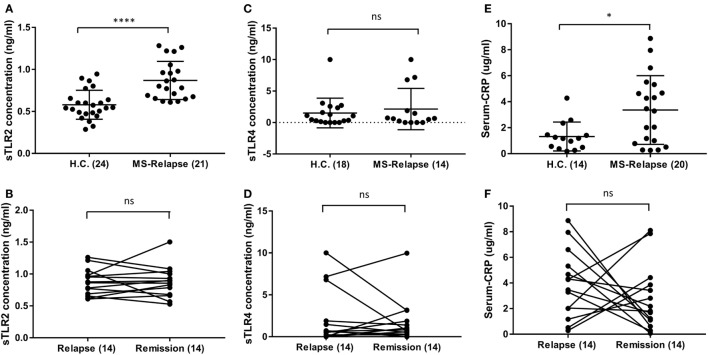
Figure 1.
Level of soluble TLR2 (sTLR2), sTLR4, and hsC-reactive protein (CRP) measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the sera of relapsing-remitting (RR) MS (RRMS) patients and compared with HC. The data are presented as mean ± SD. (A) sTLR2 measured in the serum samples from RRMS patients during relapse (n = 21) and compared with HC (n = 24). Mann–Whitney test showed significantly higher sTLR2 values during relapse (P < 0.0001). Significantly higher sTLR2 values were also observed during remission (n = 21) compared to HC (P = 0.0002) (not shown). (B) Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test between paired relapse and remission samples showed no significant difference (n = 14, P = 0.9032). (C) sTLR4 measured in the serum samples from RRMS patients during relapse (n = 14) and compared with HC (n = 18). Mann–Whitney test showed no significant differences (P = 0.9926). Comparison between remission (14) and HC also showed no significant difference (P = 0.0860) (not shown). (D) Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test between paired relapse and remission samples showed no significant difference (n = 14, P > 0.9999). (E) Serum CRP measured in the samples from RRMS patients during relapse (n = 20) and HC (n = 14). Mann–Whitney test showed significantly higher CRP during relapse (P = 0.0352) compared to HC. No significant difference observed between HC vs remission samples (not shown). (F) Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test between paired relapse and remission samples showed no significant difference (n = 14, P = 0.4263). * P < 0.05, **** P < 0.0001, ns, not significant.