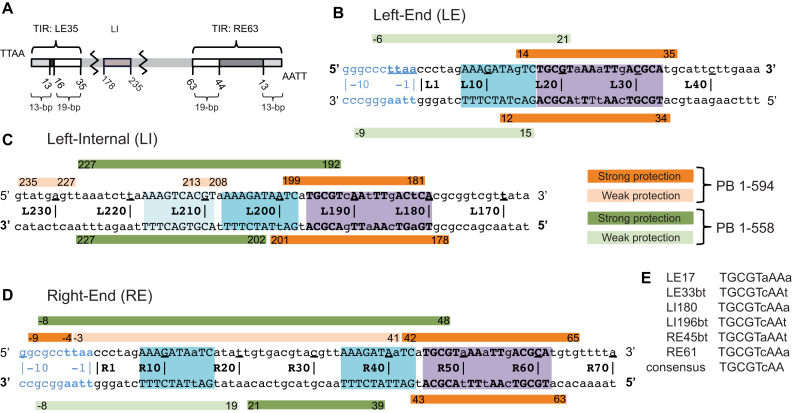
Figure 2.
Summary of DNase I footprinting results. (A) Schematic representation of the piggyBac transposon. The piggyBac left (LE1–35) and right (RE1–63) ends consist of a 13-bp terminal inverted repeat (light gray) and a 19-bp internal inverted repeat (white) separated by a 3-bp spacer and a 31-bp spacer respectively. The left internal domain (LI178–235) is highlighted in light brown. (B) Left-End (LE), (C) Left-Internal (LI) and (D) Right-End (RE) protection from DNase I cleavage in presence of full-length protein PB(1–594) (in orange) or truncated PB(1–558) which lacks the CRD (in green). Strong and weak protections are indicated by dark and light bars, respectively. Purple boxes highlight the 19-bp internal inverted repeat targeted by the PB CRD, and the blue boxes the DNA sequence that interact with the truncated PB(1–558). The DNA sequences are numbered from the TTAA target sequence that flanks each transposon end. (E) Comparison of the conserved palindromic DNA sequences belonging to the 19-bp repeat of the LE, LI and RE fragments. In (B–E), the conserved nucleotides between the three LE, LI and RE DNA segments are in uppercase and the others in lowercase. The 5′ to 3′ top strand direction is noted with 5′ and 3′ in bold in (B–D).