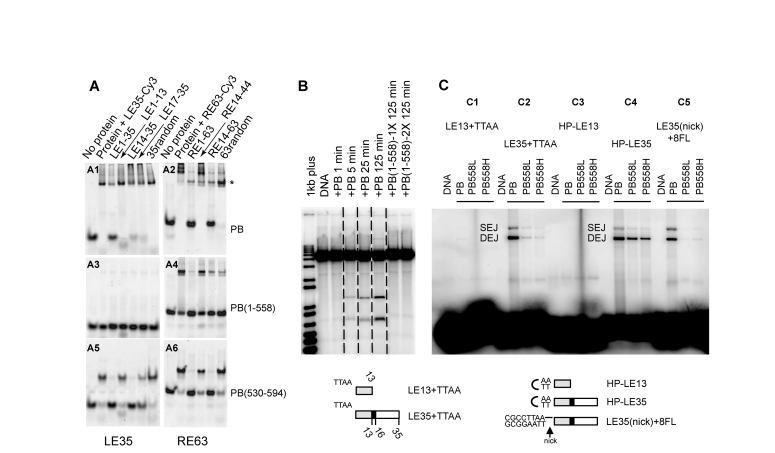
Figure 3.
Role of the C-terminal domain of PB. (A) PB specifically binds its LE-TIR and RE-TIR. For each panel, the first lane is labelled DNA in the absence of protein, and the second lane is upon incubation with either LE35-Cy3 (LE35 for LE1–35) (A1, A3, A5) or RE63-Cy3 (R63 for RE1–63) (A2, A4, A6) (50 nM final concentration). The remaining lanes in each panel indicate the effect of adding various unlabelled competitor DNA oligonucleotides indicated at the top of the figure. The protein is either the full-length PB(1–594) (A1, A2), PB(1–558) (A3, A4) or PB(530–594) (A5, A6) (1 μM final concentration). (B) In vitro cleavage assay. All samples were run on the same gel, and dashed lines indicate where different lanes were combined to prepare the figure. PB was at a final concentration of 0.59 μM, and PB(1–558) 1X and 2X correspond to 0.78 μM and 1.57 μM, respectively. (C) Target joining of LE-TIR oligonucleotide substrates: LE13+TTAA (C1), LE35+TTAA (C2), HP-LE13 (C3), HP-LE35 (C4), LE35(nick)+8FL (C5), into a target plasmid. The Single End Join (SEJ) and Double End Join (DEJ) products were visualized on a native agarose gel. Either PB (0.59 μM) or PB(1–558) at 1.25 μM (’L’ for low concentration) or 6.3 μM (’H’ for high concentration) was used. Schematic representation of LE13+TTAA, TE35+TTAA, HP-LE13, HP-LE35, LE35(nick)+8FL (a phosphodiester bond is present between the 5′-CGCCTTAA-3′ sequence and the LE35 top strand but not between the complementary sequence of 5′-CGCCTTAA-3′ and the LE35 bottom strand; the black horizontal line indicates the intact phosphodiester bond).