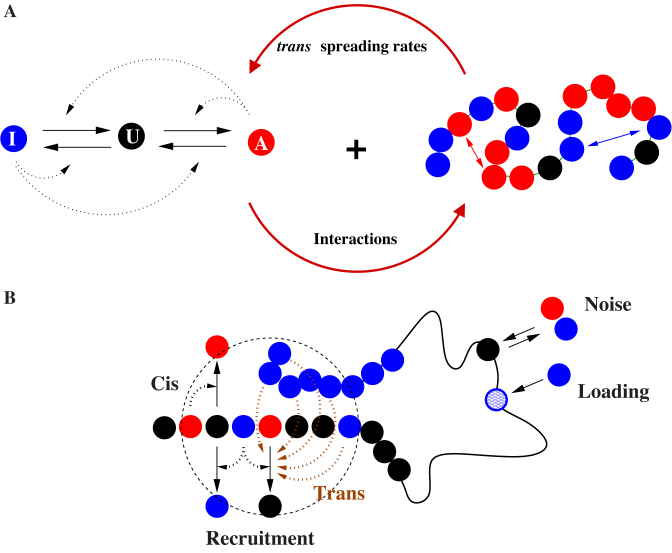
Figure 1.
The Living Chromatin model. (A) The LC model is a combination of the copolymer model (34,35) (right) and of the epigenome regulation model (26,28) (left). Each monomer can be in one of the three states: A, U and I; the inter-conversion dynamics between these states results from random or recruited (in cis or in trans) conversions. The chain is modeled by a semi-flexible self-avoiding bead-spring model with specific short-range attractions between monomers of the same epigenomic states (A or I). (B) Recruited conversions are achieved either by recruitment in cis (nearest-neighbor along the chain) or by recruitment in trans (3D neighborhood); there is also noisy conversion (I↔U, A↔U) and the possibility of external loading at some specific recruitment sites.