Figure 3.
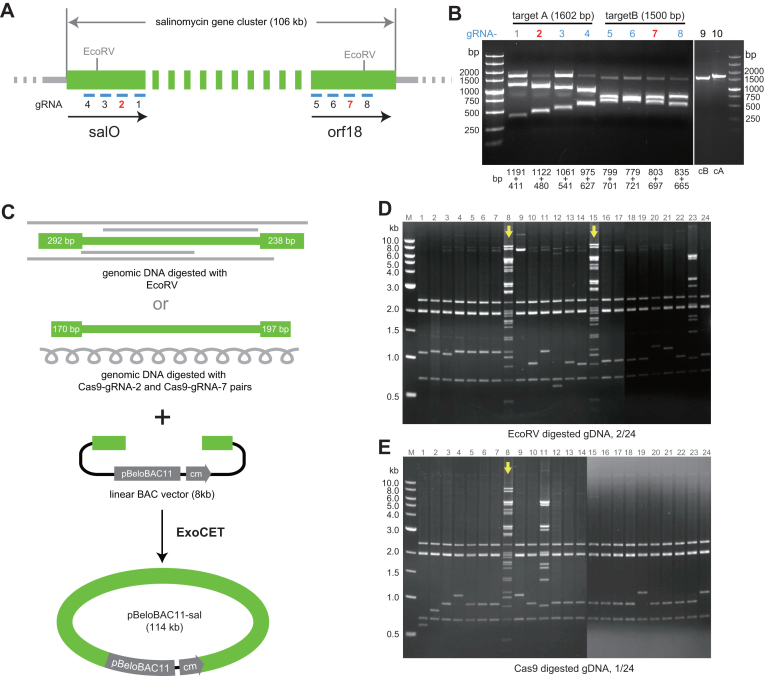
Direct cloning of the 106-kb salinomycin gene cluster from EcoRV or Cas9 digested genomic DNA of Streptomyces albus. (A) Positions of EcoRV sites and eight Cas9 guide sequences on the salinomycin gene cluster. (B) In vitro cleavage with the eight Cas9–gRNAs to evaluate gRNA efficiency on PCR products amplified from the cleavage sites; gRNAs 2 and 7 were selected. cB (lane 9) and cA (lane 10) are negative controls with Cas9 and without gRNA. (C) The salinomycin gene cluster released from genomic DNA with EcoRV or Cas9–gRNA2/Cas9–gRNA7 was cloned into the pBeloBAC11 vector using ExoCET. Homology arms (blue) had been inserted into the BAC as previously described (6) and then cleaved with BamH1 to generate the illustrated direct cloning vector. The amount of sequence overlap between the ends of the genomic DNA and vector is indicated at the ends of the genomic DNA. (D and E) PvuII restriction analysis of the recombinant DNA obtained with ExoCET cloning. Correct clones are indicated with arrows.