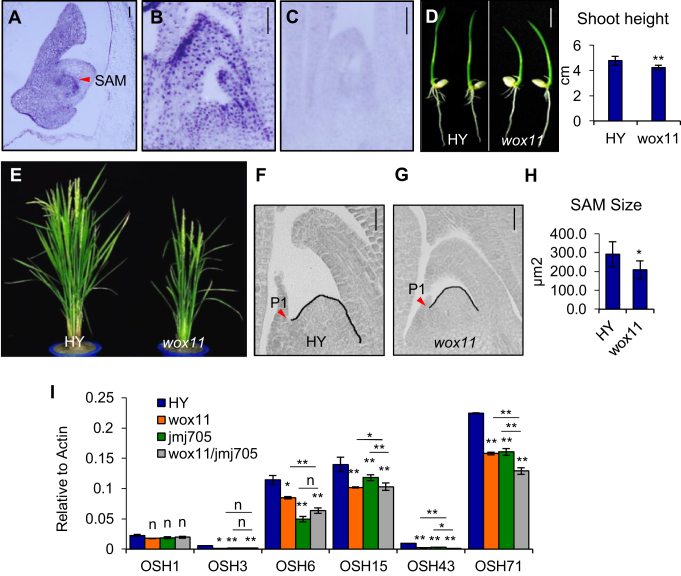
Figure 1.
WOX11 is involved in plant shoot development. (A–C) In situ hybridization detection of WOX11 transcripts in developing embryo (4 days after fertilization) (A) and 5-day-old shoot apex (B) with an antisense or a sense probe (C). Embryonic SAM in (A) is indicated by a red arrow. Bar = 50 μm. (D) Phenotype of wild type (HY) and wox11 at 7 days after germination (left), shoot height measures are shown on the right. Bar = 1 cm. **P < 0.01, t-test, two-sided (N = 30). (E) Morphology of HY and wox11 at heading stage in the field. (F and G) Shoot apex sections of HY and wox11 at 5 days after germination. Black line traces the SAM contour between leaf primordia P1 and P2. Red arrow indicates P1 leaf primordia. Bar = 20 μm. (H) Statistical analysis of HY and wox11 SAM size determined by measuring the dome area delimited by drawing a straight line between the basal edges of the two opposing youngest leaf primordia. *P < 0.05, t-test, two-sided (N = 10). (I) qRT-PCR analysis of OSH genes expression (relative to Actin transcripts) in shoot apex of HY, wox11, jmj705 and the double mutant (wox11/jmj705). Bar indicates mean ± SD from three replicates. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, n, not significant, t-test, two-sided.