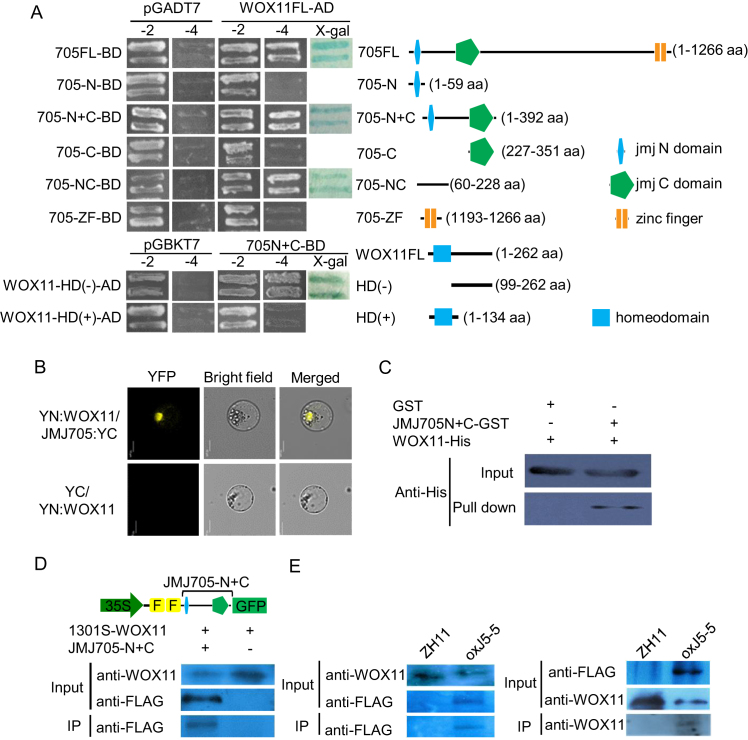
Figure 2.
WOX11 interacts with the histone H3K27me3 demethylase JMJ705 in vitro and in vivo. (A) Detection of WOX11 interaction with JMJ705 by yeast two-hybrid assay (left). Schematic structures of full length and truncated domains of JMJ705 and WOX11 were indicated on the right. (B) Interaction of WOX11 and JMJ705 in rice protoplasts. Representative cells are shown, as imaged by laser-scanning confocal microscopy. Detection in rice protoplasts of YN:WOX11 and JMJ705:YC interaction shown as yellow signal. The empty vector YC was co-expressed with YN:WOX11 and used as a control. Bar = 10 μm. (C) Pull-down assay of WOX11 and JMJ705. WOX11–6XHis was incubated with GST or JMJ705N+C-GST in GST beads and was pulled down from the JMJ705N+C-GST conjugated GST beads. (D) In vivo co-immunoprecipitation assay of WOX11 and JMJ705 interaction in tobacco. 35S-WOX11 construct was transiently transfected into tobacco leaf cells alone or co-transfected with 35S-FLAG-JMJ705-N+C-GFP. Nuclei isolated from leaves were inspected for expression of WOX11 and JMJ705 protein and then precipitated with the anti-WOX11 antibody. Anti-FLAG was used to detect the JMJ705 protein by western blots. (E) In vivo co-immunoprecipitation assay of WOX11 and JMJ705 interaction in rice. Nuclei isolated from wild type (ZH11) and JMJ705-FLAG (oxJ5–5) calli were precipitated with anti-WOX11 (left) and anti-FLAG antibodies (right) and analysed by immunoblots with anti-FLAG to detect the JMJ705 protein (left) and with the anti-WOX11 antibody to detect the WOX11 protein (right).