Fig. 1.
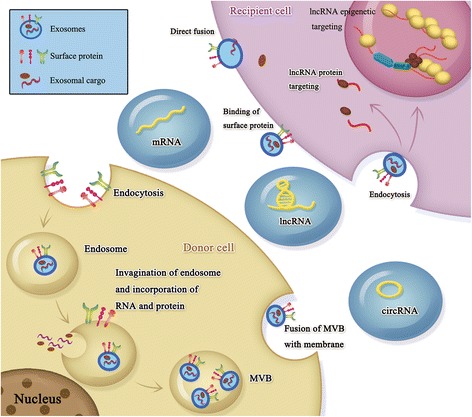
The biogenesis of exosomes. Beginning with endocytosis, the biogenesis of exosomes initially leads to the formation of endosomes. Further invagination of the endosomal membrane results in the incorporation of cytosolic protein or RNA within the endosome. The resulting multi-vesicular bodies (MVBs) then fuse with the plasma membrane and release the exosomes into the extracellular space, allowing the exosomes to interact with the recipient cells via endocytosis, direct fusion, or the binding of surface proteins. Once inside the recipient cells, RNA content, such as lncRNAs, can target proteins or epigenetic marks—affecting protein function and controlling the state of gene expression
