Fig. 2.
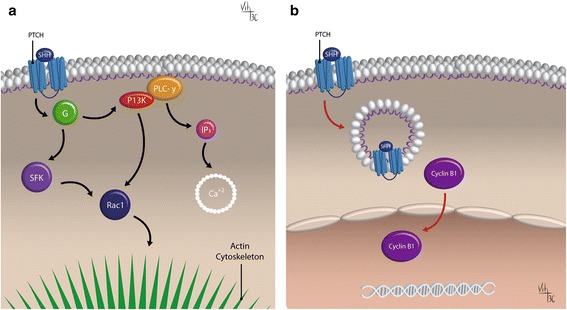
The non-canonical activation of Shh pathway. The non–canonical activation occurs through Gli-independent mechanisms and it can be of two types. A) Type I which modulates Ca2+ and actin cytoskeleton (left). When Shh binds the receptor Ptch, Smo is no longer inhibited and couple Gi proteins (G) and small GTPases RhoA and Rac1 activated. In addition, Smo stimulates calcium (Ca2+) release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and PLC-γ-catalyzed the opening of IP3-dependent channels by the generation of IP3. B) Type II which is independent on Smo. When Shh binds Ptch, the interaction of Ptch with cyclin B1 is disrupted, leading to an increase in cell proliferation and survival (right). (Diagrams by Carballo, VC). (Adapted from Robbins et al., 2012) [54]
