Figure 2.
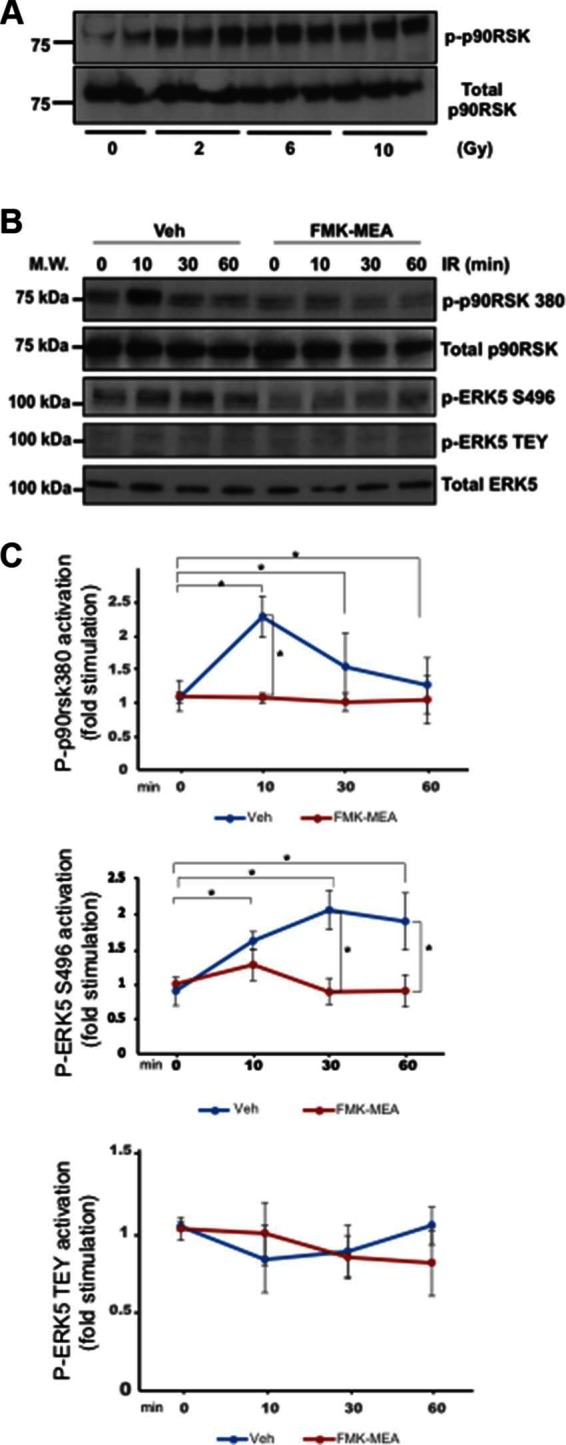
IR-induced p90RSK activation lead to ERK5 S496 phosphorylation, but not ERK5 TEY motif phosphorylation. (A) HUVECs were treated with IR by the indicated doses, and 30 min after IR, ECs were collected and p90RSK activity was detected by Western blotting with anti–p-p90RSK and anti-p90RSK antibodies. Representative images from three independent experiments are shown. (B) HAECs were pre-treated with FMK-MEA (5 µM) for 30 min and treated by IR (2 Gy) for the indicated times. ECs were collected, and total p90RSK, p90RSK phosphorylation, ERK5 S496 phosphorylation, ERK5 TEY motif phosphorylation, and total ERK5 were detected by Western blotting with anti-p90RSK, anti-phospho-p90RSK (S380), anti-phospho-ERK5 (S496), anti-phospho-ERK5 (TEY motif), and anti-ERK5. Representative images from three independent experiments are shown. (C) Quantification of IR-induced p90RSK activation (S380 phosphorylation; top), ERK5 S496 phosphorylation (middle), and ERK5 activation (TEY motif phosphorylation; bottom) is shown after normalization by total protein levels. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 3).
