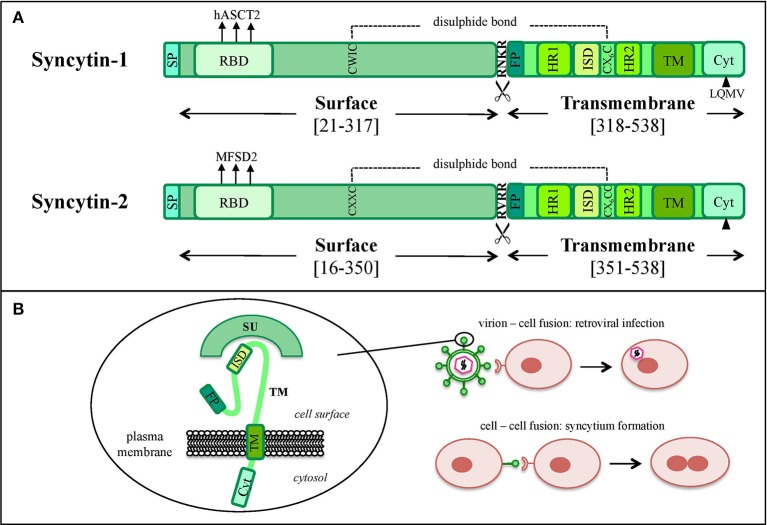
Figure 3.
Graphical comparison between syncytin-1 and syncytin-2 proteins. (A) Schematic comparison of HERV-W syncytin-1 and HERV-FRD syncytin-2. The positions of Surface (SU) and Transmembrane (TM) subunits as well as the main functional and regulatory domains relevant for the protein's physiological activities are reported: signal peptide (SP), receptor binding domain (RBD) and the relative main cellular receptor, fusion peptide (FP), fusion core N- and C-terminal heptad repeats (HR1 and HR2, respectively), immunosuppressive domain (ISD), transmembrane motif (TM), intracytoplasmic tail (CYT) and the relative specific deletion for protease-independent activation (black triangle). The sites involved in SU and TM disulphide bond (dashed line) and furin cleavage (scissor symbol) are also indicated. Please see the text for more details about the individual domain functions. (B) Simplified model of the protein's structural configuration and fusogenic role when inserted into viral or cellular membranes.