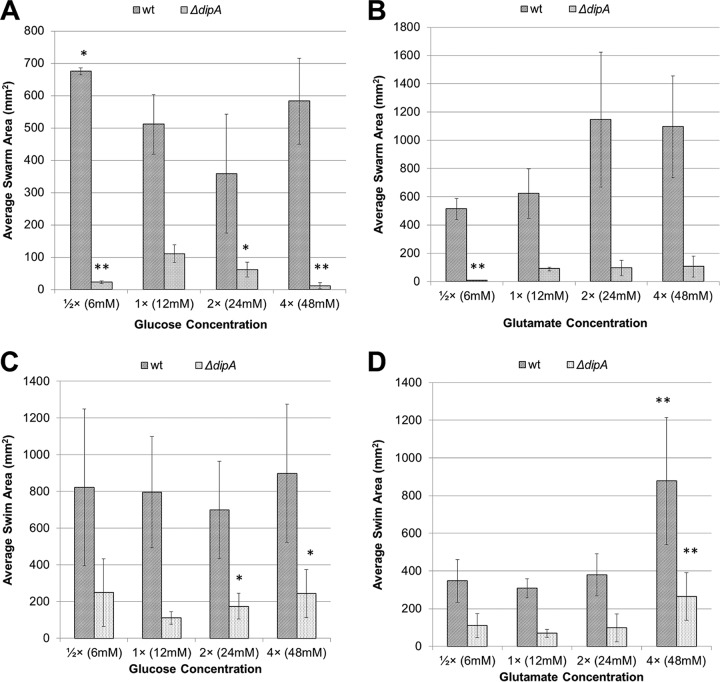
FIG 9.
Effects of carbon source concentration on average swarm and swim areas in wt and the ΔdipA mutant. (A) Lowering the glucose concentration significantly improved wt swarming. Raising the glucose concentration appeared to inhibit wt swarming, though not to a degree that was statistically significant. Both raising and lowering the glucose concentrations significantly decreased swarm areas in the ΔdipA mutant. (B) Raising the glutamate concentration generally increased swarming in the wt, though not significantly according to Student's t tests. Lowering the glutamate concentration did significantly impair swarming in the ΔdipA mutant. Raising the glutamate concentration had no effect on the ΔdipA mutant. Swimming was less affected by changes in concentration than swarming. (C) On glucose, wt swimming did not differ significantly. However, the ΔdipA mutant showed significant increases in swimming motility under the 2× (24 mM) and 4× (48 mM) conditions. (D) On glutamate, only the 4× (48 mM) concentration showed significant increases compared to the 1× concentration. This held for both the wt and the ΔdipA mutant. All plates used the FAB base medium. Error bars indicate standard deviations. *, P < 0.05 compared to wt growing under the 1× (12 mM) condition. **, P ≤ 0.01 compared to ΔdipA mutant growing under the 1× (12 mM) condition.