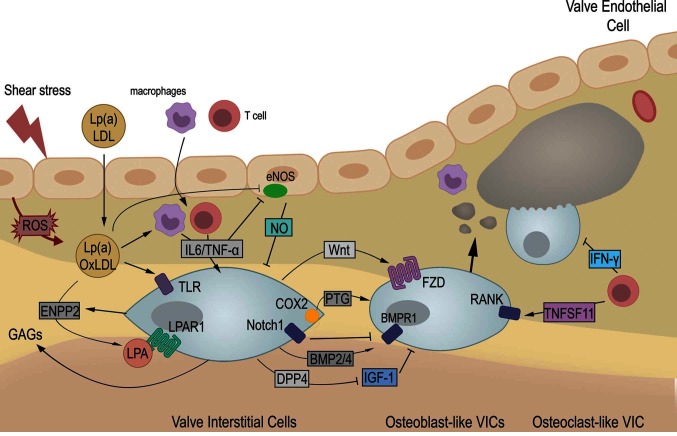
Figure 1.
CAVD is a multi-step disease. Upon valve endothelium damage, low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) and lipoprotein a [Lp(a)] accumulate. Oxidation of LDL (oxLDL) trigger infiltration of macrophages and T cells that express pro-inflammatory cytokines among which IL-6 and TNF-α. Proinflammatory cytokines impairs protective role of valve endothelial by inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and production of nitric oxide (NO). Therefore, oxidative stress (ROS) increases and contributes to enhance oxLDL. Concomitantly, valve interstitial cells (VICs) get activated by cytokines and oxLDL directly, or indirectly through autotaxin (ENPP2) and lysophosphatidyl acid (LPA). Therefore, VICs enter an osteogenic differentiation leading to calcific deposit and nodule formation. Activated VICs secrete glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), favoring further accumulation of oxLDL. Increased cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) and its product prostaglandin (PTG), Wnt and BMP signaling have been shown to drive osteogenic differentiation while inhibition of IGF-1 signaling by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) contributes as well to pathogenesis. Also, Notch signaling, induced by NO, repress osteogenic differentiation. Finally, T cells favor osteogenesis and osteoclast formation by production of TNFSF11 but secrete Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) which limits calcium resorption. Altogether, aortic valve leaflets gets remodeled and stiffen leading to aortic valve stenosis. ROS: Reactive Oxygen Species. LPAR1: Lysosphosphatidyl Acid Receptor 1. TLR: Toll-like receptor. IL6: interleukin 6. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor- α. BMP: Bone Morphogenetic Protein. Morphogen. BMPR1: BMP Receptor 1. Fzd: Frizzled. RANK: Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor kB. TNFSF11: RANK ligand.