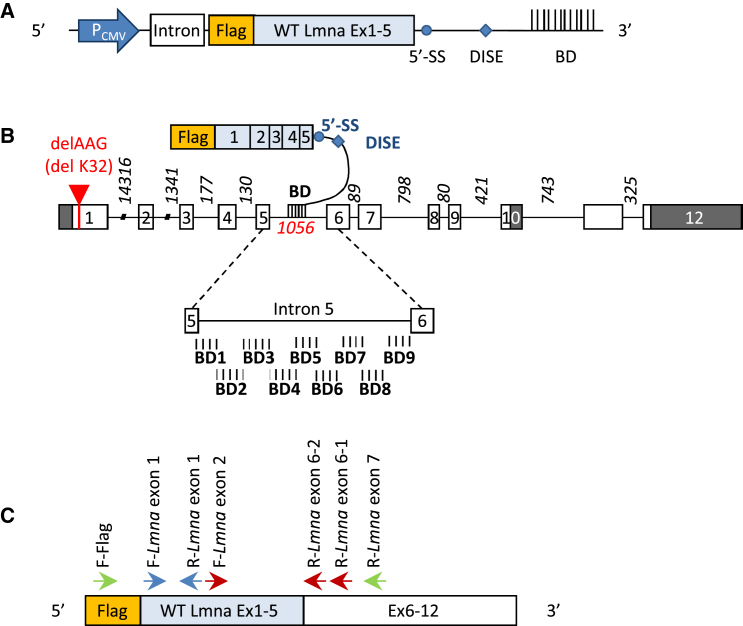
Figure 1.
5′ Trans-Splicing Strategy for Lmna Transcripts
(A) Schematic illustration of part of the vector encoding for a pre-trans-splicing molecule (PTM). The PTM is a transcript comprising the FLAG coding sequence followed by the first five Lmna exons (WT Lmna ex 1–5), a 5′ splice site (5′SS) followed by a downstream intronic splicing enhancer (DISE), and a binding domain (BD) of 150 bp complementary to Lmna intron 5. PTM sequences are placed under control of a CMV promoter (PCMV). An intronic sequence was added to stabilize the transcript. (B) Schematic representation of Lmna pre-mRNA and PTMs. The mouse Lmna pre-messenger consists of exons (boxes) and introns (lines). White boxes represent coding sequences, and gray boxes represent non-coding sequence for prelamin A. Intronic size lengths are indicated. The red arrow refers to localization of the ΔK32 mutation in exon 1. Below, an enlarged view of intron 5 shows the localization of the different designed binding domains. (C) Schematic representation of a trans-spliced mRNA molecule and the different primers used to characterize trans-spliced/repaired mRNA (F-FLAG and R-Lmna exon 7), PTMs (F-FLAG and R-Lmna exon 1), and total (endogenous and trans-spliced) Lmna molecules (F-Lmna exon 1 and R-Lmna exon 1). Primers used for nested qPCR of trans-spliced Lmna transcripts are F-FLAG and R-Lmna exon 6-1 for the first PCR, followed by F-Lmna exon 2 and R-Lmna exon 6-2 for the qPCR.