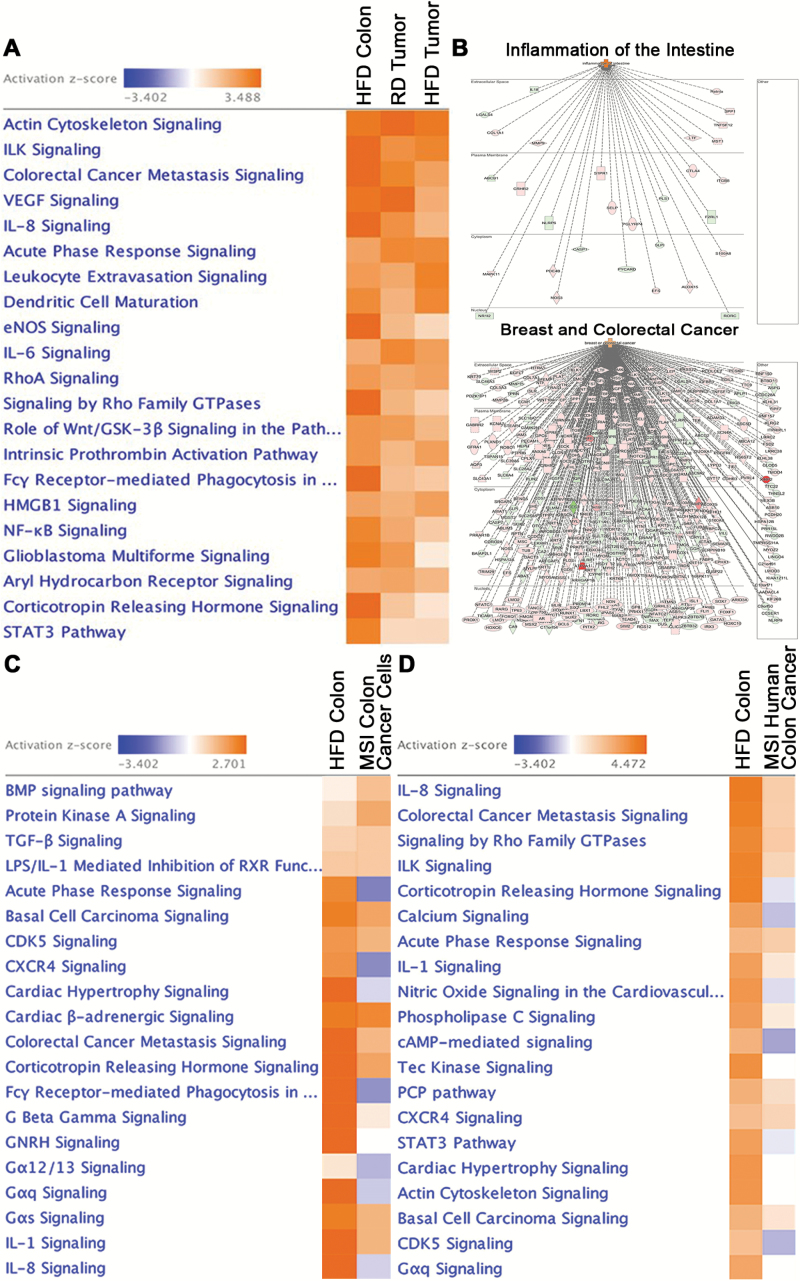
Figure 3.
HFD activates pathways involved in inflammation and carcinogenesis similar to those associated with microsatellite instability. (A) Top canonical pathways activated in colon of mice on HFD and tumors (RD and HFD) relative to colon on RD (FDR < 0.05, IPA). (B) Disease and function analysis of the differentially expressed transcripts revealed their association with intestinal inflammation and breast and colorectal cancer (activation color score: red: ↑ expression, green: ↓ expression) (FDR < 0.05, IPA). (C) Pathway analysis revealed that the transcriptional signature obtained from mouse HFD colon shared a high degree of similarity with MSI human colorectal cancer cell lines. The MSI colon cancer cell line expression signature was generated by comparing RNA-seq from 5 inflammatory MSI cell lines (HCT15, LoVo, LS411N, RKO, SW48) against 5 non-inflammatory MSS cell lines (SW480, SNUC1, HT55, HT29, COLO-201) (27) using EBseq (FDR < 0.05, IPA). (D) Pathway analysis revealed that the transcriptional signature obtained from mouse HFD colon shared a high degree of similarity with human MSI colon cancer. The MSI colon cancer expression signature was generated by comparing RNA-seq from human MSI against MSS colon cancers (TCGA) using EBseq (FDR < 0.05, IPA).