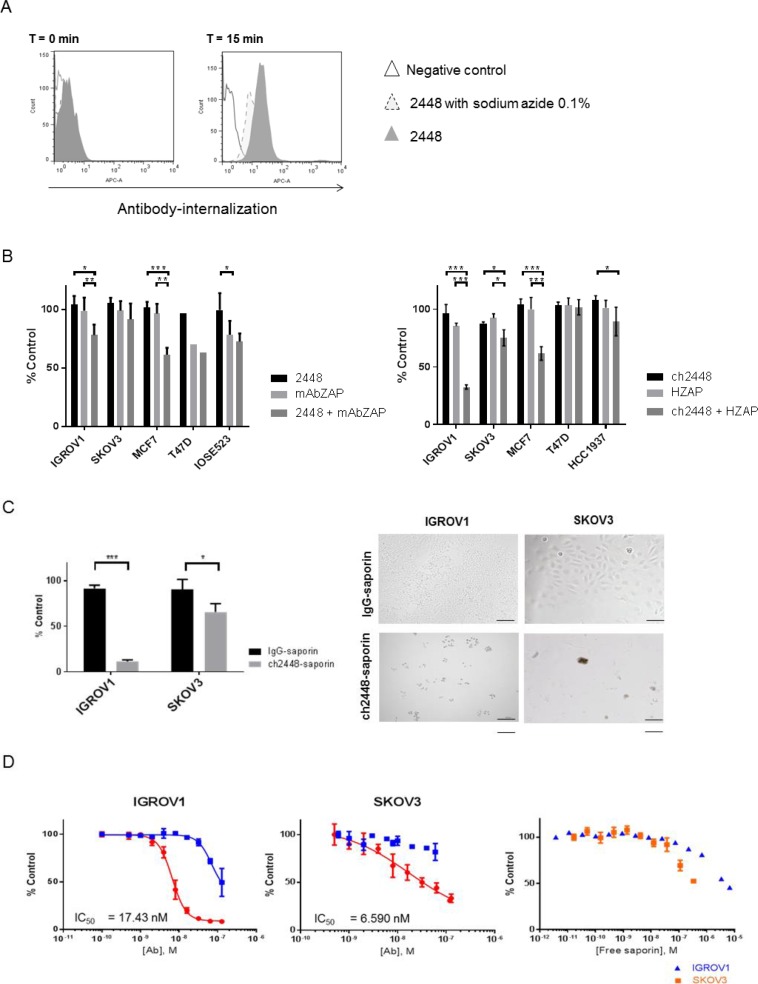
Figure 3. Delivery of cytotoxic payloads by 2448 and ch2448.
The potential of 2448 to be developed as an ADC was assessed. (A) Antibody 2448 was labelled with Cypher5e dye that maximally fluoresces in low pH environments (such as endosomal and lysosomal cellular compartments). At 4° C, IGROV1 cells were pre-incubated with dye-conjugated 2448 in the presence or absence of sodium azide (or with dye alone as a negative control). At T = 0 min, the temperature of samples was raised to 37° C. At T = 15 min, 2448 internalization was observed by an increase in fluorescence intensity. Less antibody internalization was observed on cells pre-treated with sodium azide as indicated by lower fluorescence intensity. (B) The cytotoxic effects of mAbs in-complex with secondary saporin conjugates (ZAP) was evaluated. Primary 2448 and ch2448 were pre-mixed with anti-mouse IgG (mAbZAP) and anti-human IgG saporin conjugates (HZAP), respectively. Ovarian and breast cancer cells were incubated with mixtures, primary antibody alone (2448 or ch2448), saporin conjugate alone (mAbZAP or HZAP) or buffer as a vehicle control. Post 72 h incubation, a significant cytotoxic effect was measured in IGROV1 and MCF7 cells that were treated with mAbs in-complex with secondary conjugates compared to cells treated with primary mAb or secondary conjugate alone. (C) IGROV1 and SKOV3 were treated with saporin-conjugated ch2448 (ch2448-saporin) or isotype control (IgG-saporin) at 30 mM. Cell viability was measured as a percentage of cells treated with buffer alone (% control). Post 72 h incubation, an 80% and 30% decrease in viability was observed on IGROV1 and SKOV3 cells, respectively. Cells treated with ch2448-saporin had shriveled unhealthy morphologies as observed by bright-field microscopy. Results were represented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments with triplicate. (D) Dose-dependent cytotoxicity of ch2448-saporin was evaluated. Post 72 h incubation, greater cytotoxicity was observed for ch2448-saporin than the IgG-saporin control. IC50 values of 6.59 nM and 17.43 nM were calculated on IGROV1 and SKOV3 cells, respectively. Cytotoxicity of free saporin was observed at higher concentrations (> 0.1 µM). For (B) and (C), the relative cell viability was measured as a percentage of cells treated with buffer alone (% control). Results were represented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was measured by a two-sided unpaired Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; and ***p < 0.001). For (D), values were means ± standard deviations of biological triplicates. Non-linear regression was performed to determine the IC50 values using GraphPad Prism 6. Similar IC50 values were observed in two independent experiments.