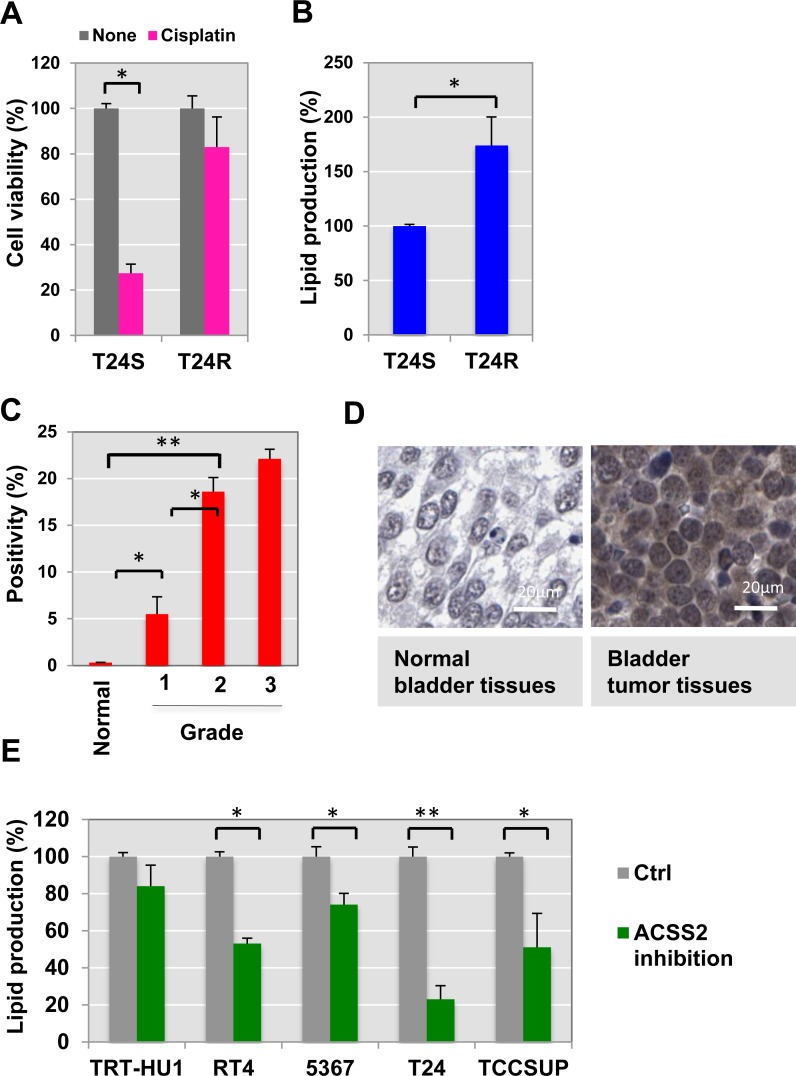
Figure 1. Cisplatin resistance is associated with ACSS2.
(A) Cisplatin resistant T24R cells showed a delayed apoptosis in response to cisplatin treatment, compared to T24S. Cell viability was measured in the absence or presence of cisplatin media for 2 days. *p < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). (B) Total lipid levels of T24R were compared to T24S cells. **p < 0.005 (C–D) ACSS2 expression increased in bladder cancer tissues in comparison of normal bladder tissues. (C) The BC TMA was stained with anti-ACSS2 antibody (1:100) as described in the Materials and Methods section. The expression levels of ACSS2 were examined and quantified based on positivity of staining as previously described. (D) Images of one representative example of staining in normal noncancerous bladder tissue (left), and one representative example of staining in the paired bladder tumor tissues from same patients (right) were shown. (E) ACSS2 inhibition decreased total lipid contents in a series of BC cells. Cells were incubated with ACSS2 inhibitor-containing media for 20 hrs, which was followed by lipid measurement as described in Methods. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005 (Student’s t-test).