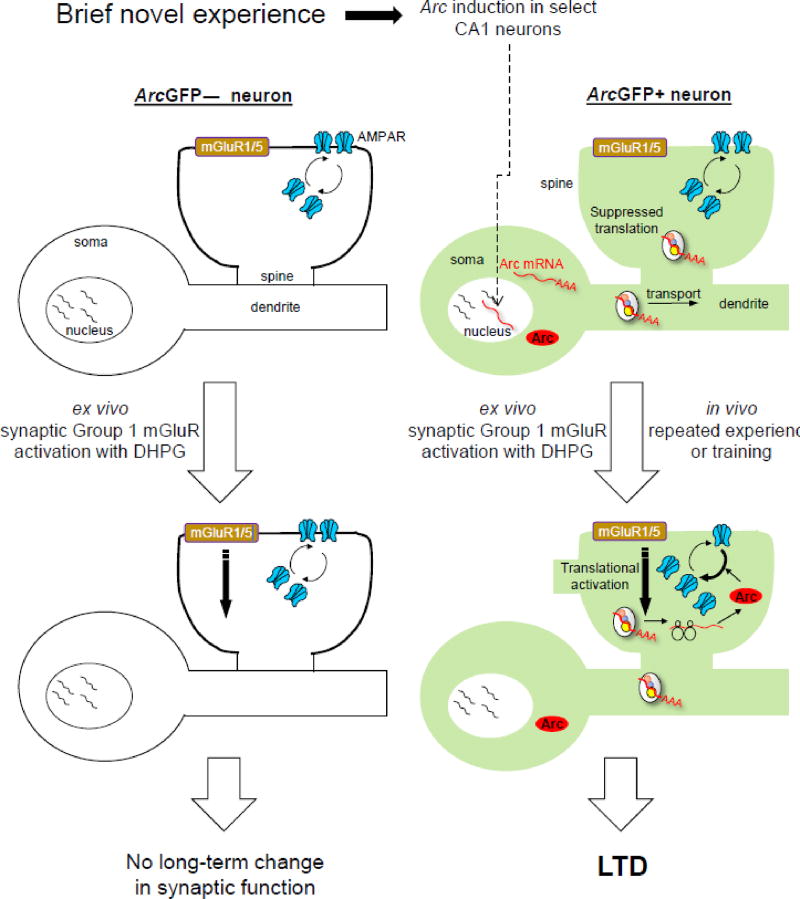
Figure 1. Proposed model of mGluR-LTD priming by novelty-induced Arc in hippocampal CA1 neurons based on data from [20].
A novel experience induces transcription of Arc mRNA in a select population of CA1 neurons (ArcGFP+). After induction, Arc mRNAs are transported to dendrites where evidence suggests it is translationally suppressed [31, 48, 50]. Ex vivo activation of group 1 mGluRs (in slices) activates Arc translation in dendrites, of those neurons with recent Arc mRNA induction (ArcGFP+), but not neighboring ArcGFP(−) neurons [13, 14]. Arc protein increases the endocytosis rate of AMPA receptors, causing long-term synaptic depression only in ArcGFP+ neurons. Repeated experience of the same environment reactivates synapses on the same neurons initially activated when the environment was novel and Arc mRNA was induced (ArcGFP+) [1] which is proposed to suppress synaptic transmission onto these neurons in vivo through a similar mechanism as LTD. Modified from [20].