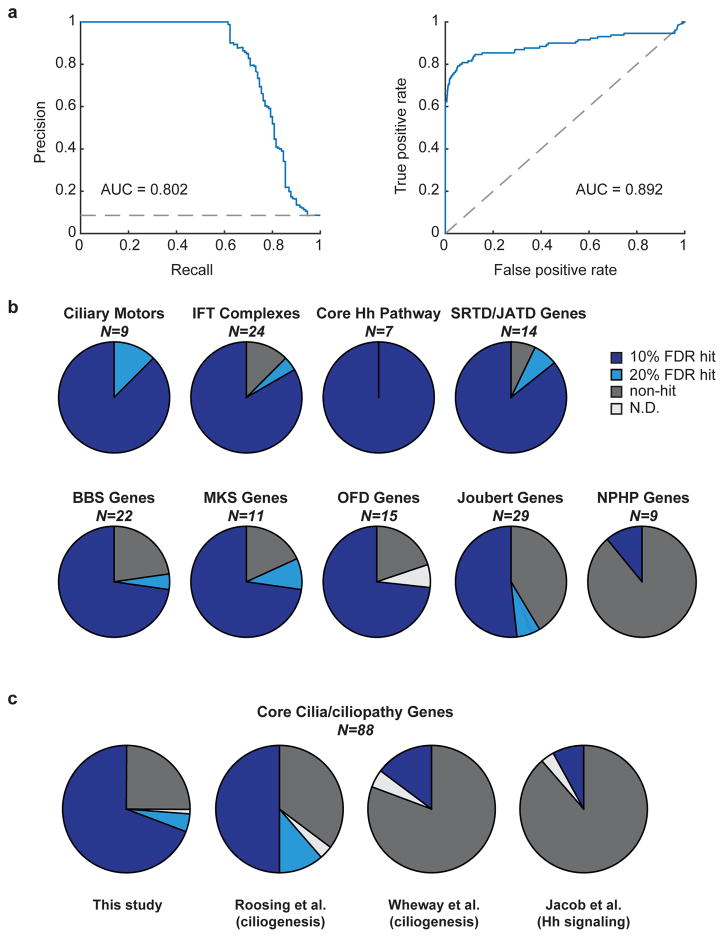
Figure 3. Evaluation of screen performance.
a) Assessment of screen performance using 130 positive and 1386 negative reference genes, as determined by precision-recall analysis (left) and ROC curve (right), with the area under each curve (AUC) shown. Dashed lines indicate performance of a random classification model. b) Analysis of hit gene detection for select gene categories (N = number of genes in each category), with the fraction of hits detected at 10% or 20% FDR, not detected, or not determined shown; see Supplementary Table 3 for details. The NPHP category includes genes mutated exclusively in NPHP and not other ciliopathies. Abbreviations: SRTD (short rib thoracic dysplasia), JATD (Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia), OFD (Oral-Facial-Digital Syndrome). c) Hit gene identification is compared for the indicated datasets. Pie charts show the fraction of N=88 genes detected as hits across all genes included in part (b), except the NPHP-specific category; see Supplementary Fig. 3a for detail among individual categories.