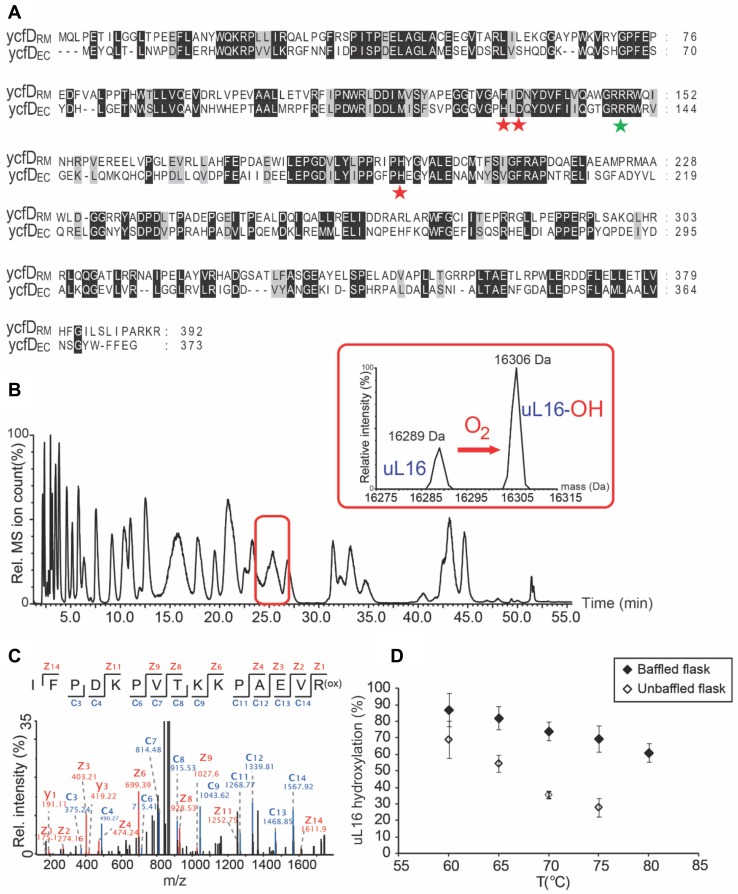
Fig. 1.
ycfDRM from R. marinus catalyses oxygen-dependent ribosomal protein hydroxylation. a Protein sequence alignment of ycfDRM and ycfDEC produced with ClustalW and edited using GeneDoc 2.7. Red stars in a indicate the Fe(II)-binding facial triad and the green star indicates the basic residue that binds 2OG. b Ribosomal proteins were isolated by sucrose density centrifugation followed by acetone precipitation. UPLC protein separation coupled to ESI-TOF mass spectrometry was used to chromatographically separate and determine the intact masses of R. marinus ribosomal proteins. Inset: deconvoluted ESI–MS spectrum showing partial hydroxylation of ribosomal protein uL16RM. c MS/MS spectrum of uL16RM fragment showing hydroxylation at R82; d Hydroxylation of uL16RM decreases with an increase in growth temperature of R. marinus and varies for growth in baffled (2.5 L polypropylene filled to 1 L with media) and unbaffled flasks (2 L Pyrex filled to 0.6 L with media). uL16RM intact protein masses were determined by ESI–MS spectrometry. Average of two independent MS experiments is shown with error bars denoting standard deviation of the mean. Deconvoluted MS spectra are shown in Supplementary Materials