Figure 5.
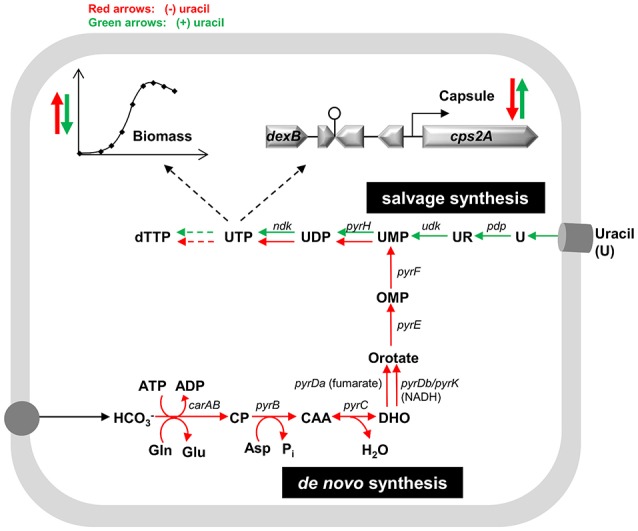
Proposed model for the effect of uracil on pyrimidine metabolism, biomass and capsule production in S. pneumoniae. The intracellular reactions depicted are catalyzed by the following enzymes (the genes that code for the enzymes are in parenthesis): carbamoyl-phosphate synthase, small and large subunit (carAB), aspartate carbamoyltransferase (pyrB), dihydroorotase (pyrC), dihydroorotate dehydrogenase A (pyrDa), dihydroorotate dehydrogenases (pyrDb-pyrK), orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (pyrE), orotidine 5-phosphate decarboxylase (pyrF), uridylate kinase (pyrH), pyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylase (pdp), uridine kinase (udk), nucleoside-diphosphate kinase (ndk). Narrower red and green arrows indicate the pathways active when uracil is absent and present, respectively. Bold red and green arrows pointed up indicate an increase in biomass and capsule expression in the absence or presence of uracil, respectively, whereas pointed down arrows indicate a decrease. Asp, aspartate; CAA, carbamoyl-aspartate; CP, carbamoyl-phosphate; DHO, dihydroorotate; Gln, glutamine; Glu, glutamate; , bicarbonate; OMP, orotate monophosphate; Pi, inorganic phosphate; U, uracil; UR, uridine. The nomenclature for the nucleotide abbreviations are provided in the list of abbreviations of this manuscript.
