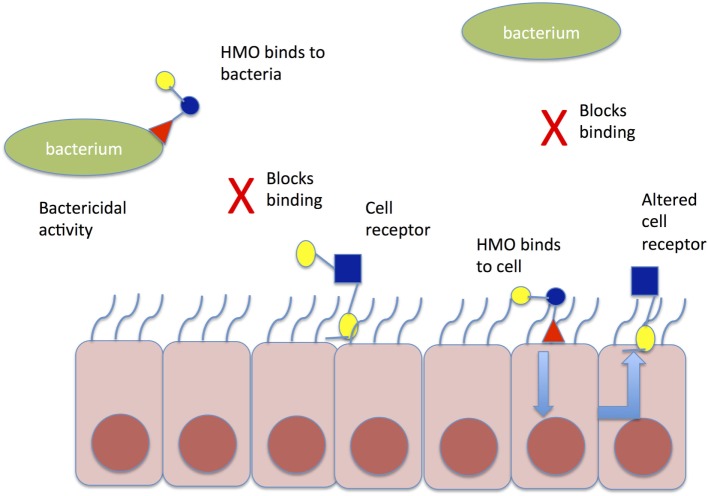
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of HMO to prevent aberrant pathogen colonization. HMO may bind directly to bacteria in the gut lumen causing conformational change in bacterial binding sites and preventing binding to cell receptors; alternatively, HMO may bind directly to gut epithelial cells causing altered expression of cell receptors, which prevent pathogen binding to gut epithelial cells. HMO, human milk oligosaccharide.