Fig. 2.
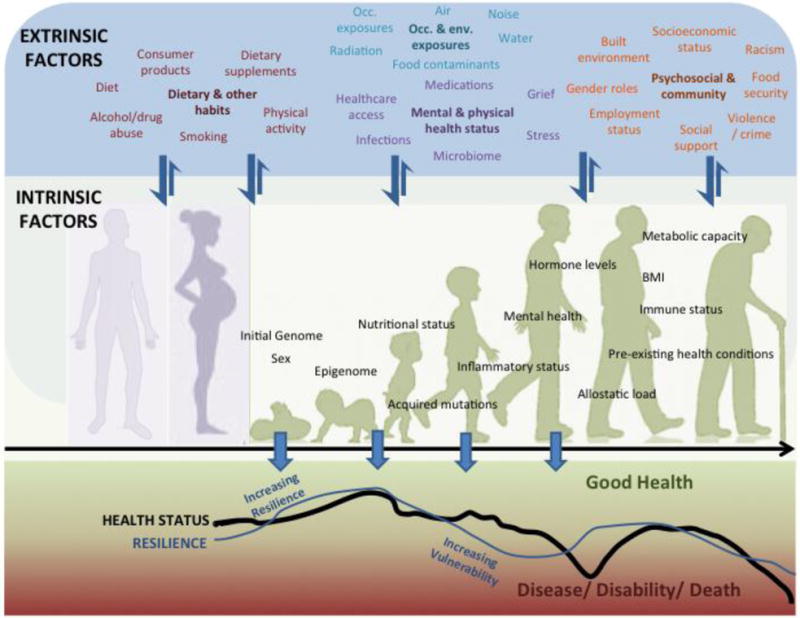
Extrinsic (E, upper panel) and intrinsic (I, middle panel) factors interact throughout the lifespan, enhancing vulnerability or resilience in a cumulative manner. Intrinsic genome and sex are fixed I factors whereas the other I factors are modifiable. Many E factors act on and influence the I factors, whereas E factors are modulated to a lesser degree by I factors (indicated by thick and thin arrows between the upper and middle panels). I×E interactions can vary over the lifespan beginning before conception via maternal and paternal effects (background schematic in middle panel). In a given individual, I×E interactions influence vulnerability and resilience, and consequentially health status, throughout life, as indicated by the fluctuating curves in the lower panel. The curves shown are not based on actual data and are hypothetical trajectories indicative of negative and positive effects on resilience and health status over the lifespan. Scenarios that could contribute to these fluctuations are described in the text in Section 3. Occ., occupational; Env., environmental.
