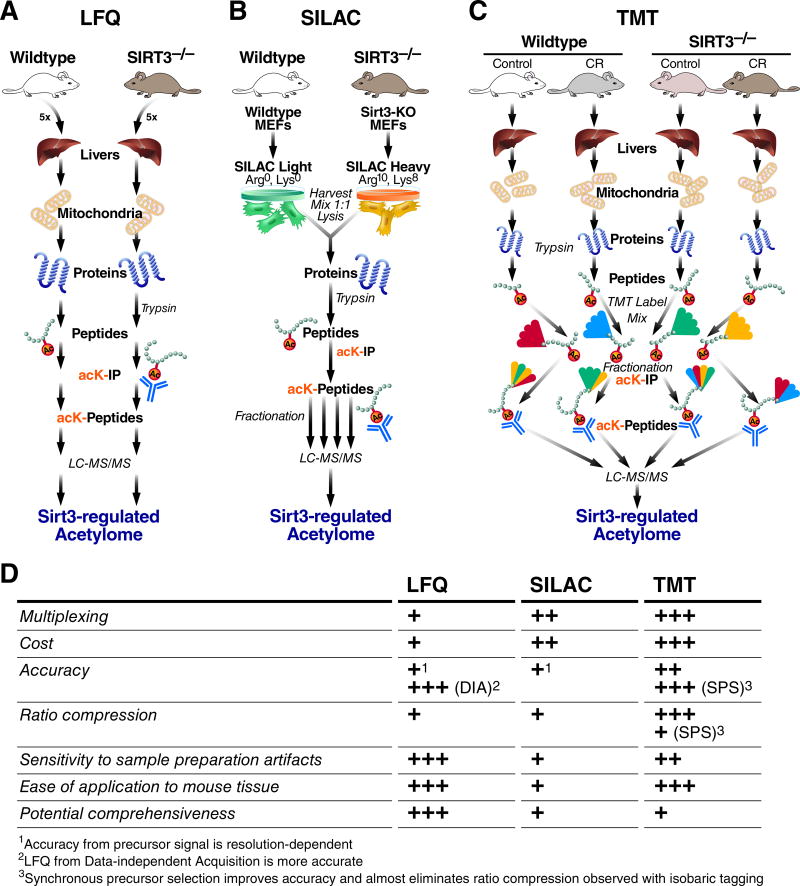
Figure 1. Mass Spectrometry Methods for Relative Quantification of Site-Specific Protein Acylation.
Workflows pictured here reflect the respective studies from the text, and are representative of the most common strategy although slight variations are used. The number of arrows along each workflow indicates where sample mixing occurs, if at all. A, Workflow for Label-Free Quantification (LFQ). B, Workflow for metabolic labeling of MEFs from mutant mice using SILAC. C, Workflow for in vitro isobaric labeling of peptides using TMT reagent. D, Comparison of relative strengths and weaknesses among the methods in (A–C). All strategies use protein isolation, trypsin digestion, immuno-affinity enrichment of the low-abundance peptides containing acetyl-lysine, and LC-MS/MS for identification and quantification. All strategies can be combined with fractionation before LC-MSMS to increase the number of identified acetylation sites, but this greatly complicates LFQ data analysis.