Figure 5.
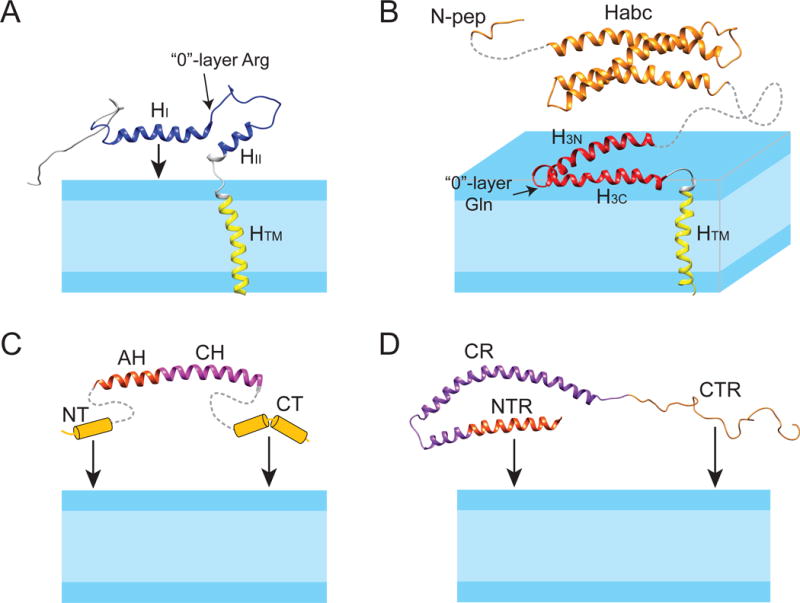
Structure models of synaptobrevin, syntaxin, complexin, and α-synuclein in lipid bilayer membranes. (A) Solution NMR structure of synaptobrevin in DPC (PDB code: 1KOG); (B) full-length syntaxin: solution NMR structure of syntaxin (residues 183-288) in DPC (PDB code: 2M8R) is linked with the NMR structure of the soluble Habc domain (residues 27-146) (1BR0) and the N-peptide (residues 1-12) (3C98); (C) complexin: the structure of the AH and CH helices, taken from the crystal structure of the complexin/SNARE co-complex (1KIL), is linked with the presumed helix-prone N- and C-termini that can tether complexin to the membrane; (D) solution NMR structure of α-synuclein in SDS micelles (1XQ8). The NTR and CTR can tether α-synuclein to the membrane. The protein domains are colored as in Figure 2.
