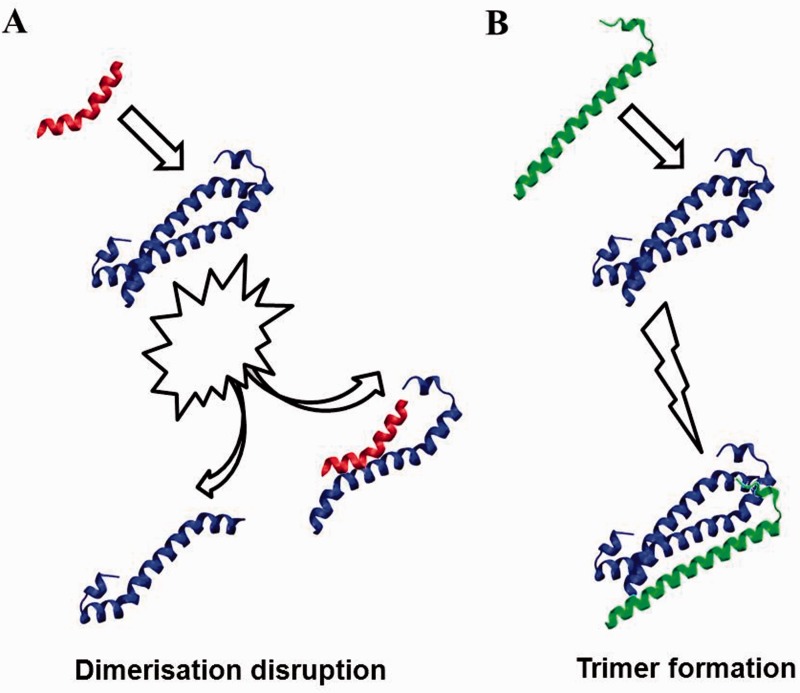
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of possible molecular mechanisms involving MST2 homodimers (blue) and tertiary binding partners. (A) Small peptides can be designed to bind competitively and disrupt SARAH homodimers. (B) Sarah domains of other kinases (e.g. RASSFn, green) may bind noncompetitively to MST monomers or homomodimers and could facilitate and/or stabilize homodimeric interactions. A colour version of this figure is available at BIB online: http://bib.oxfordjournals.org.