Fig. 1.
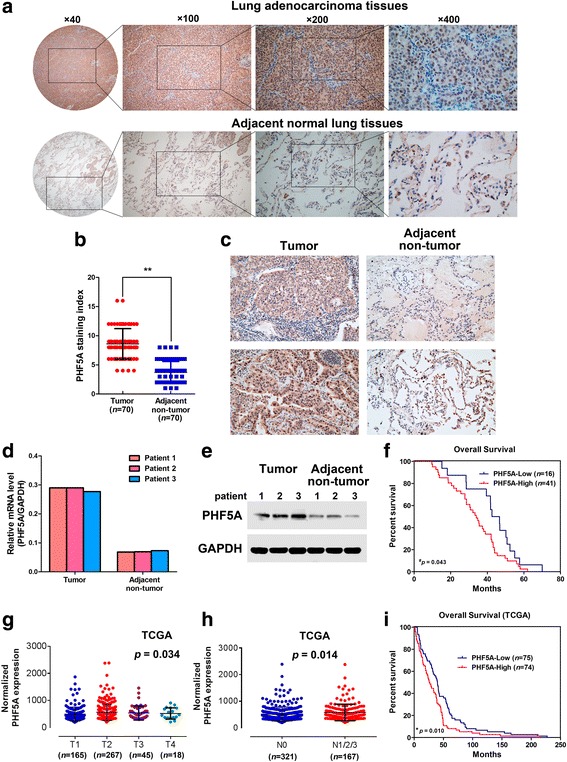
PHF5A overexpression is associated with lung adenocarcinoma (LAC) progression and poor prognosis. a PHF5A expression in LAC tissue microarrays. Representative images of LAC tissue samples with strong nuclear staining (brown), with adjacent noncancerous normal lung tissues showing weakly positive PHF5A staining. b The staining index (SI) of PHF5A expression in LAC tissues was significantly higher than that of normal paired samples. c-e PHF5A expression was confirmed in three fresh paired primary LAC tissues and matched adjacent non-tumor tissues from the same patient, by IHC (c), qRT-PCR (d) and Western blot (e). f Kaplan-Meier survival curves for LAC patients with high and low PHF5A expression levels, respectively. LAC patients with high PHF5A expression showed poorer survival compared with the low PHF5A group (n = 57; P = 0.043, # compared by Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test). g-h TCGA data indicated that Phf5a mRNA levels in LAC tissues were associated with T stage (g) and N stage (h). i Kaplan-Meier survival curves comparing LAC patients with low and high Phf5a expression levels (n = 149; P = 0.010, ★compared by the log-rank test; TCGA). High and low expression levels were based on the median value of Phf5a mRNA. **P < 0.01
