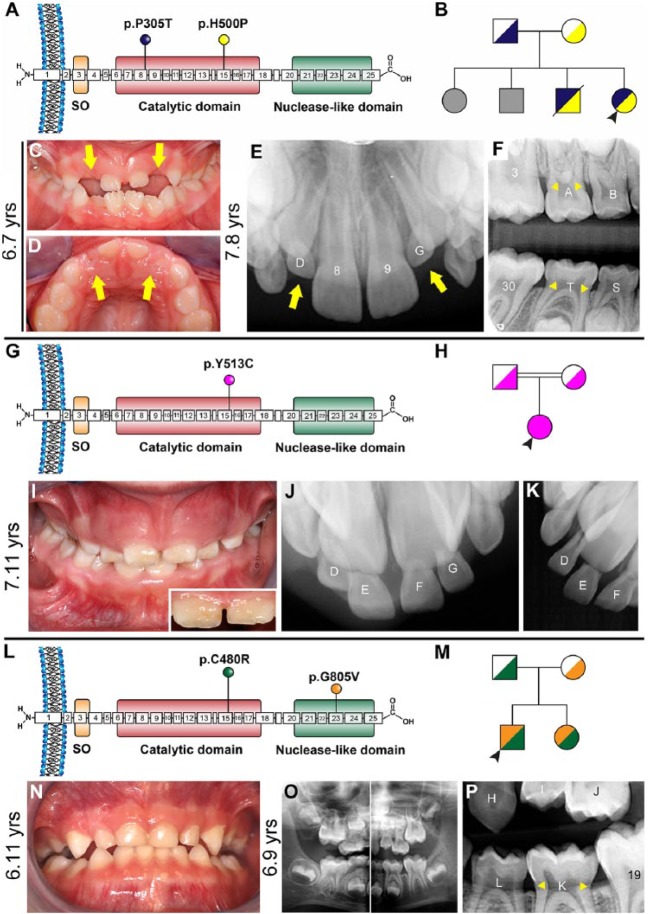
Figure 1.
Clinical presentations of generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI) subjects 1 to 3. (A) Schematic of ENPP1 protein indicating locations of p.P305T (exon 8) and p.H500P (exon 15) amino acid substitutions identified in subject 1. (B) Pedigree of proband subject 1 (black arrowhead) showing unaffected parents, 2 unaffected older siblings (unknown genetic composition indicated by gray shading), and an older brother harboring the same biallelic ENPP1 mutations who died of cardiac arrest. (C, D) Clinical photographs at 6.7 y of age reveal infraoccluded primary maxillary lateral incisors (yellow arrows). (E) Periapical radiograph at 7.8 y shows eruption of permanent maxillary incisors (8, 9) while primary lateral incisors remain infraoccluded (yellow arrows) and secondary lateral incisors are unerupted. (F) Bitewing radiograph reveals a protruding cervical root morphology (yellow arrowheads) in primary and secondary molars, where cementum sometimes appears to overlap enamel at the cementum-enamel junction. (G) Schematic of ENPP1 protein indicating the location of the homozygous p.Y513C amino acid substitution in exon 15 identified in subject 2. (H) Pedigree of proband subject 2 (black arrowhead) showing unaffected consanguineous parents. (I) Clinical photograph of subject 2 at 7.11 y reveals a mixed dentition with gingival hyperplasia and mild discoloration in enamel of central incisors (inset). (J, K) Dental radiographs indicate overretained maxillary central and lateral incisors. (L) Schematic of ENPP1 protein indicating locations of p.C480R (exon 15) and p.G805V (exon 23) amino acid substitutions identified in GACI subject 3. (M) Pedigree of proband subject 3 (black arrowhead) showing unaffected parents and younger sister with GACI. (N) Oral photograph at 6.11 y and (O) panoramic radiograph at 6.9 y reveal a healthy mixed dentition. (P) Dental bitewing radiograph shows protruding cervical root morphology on primary molar K.