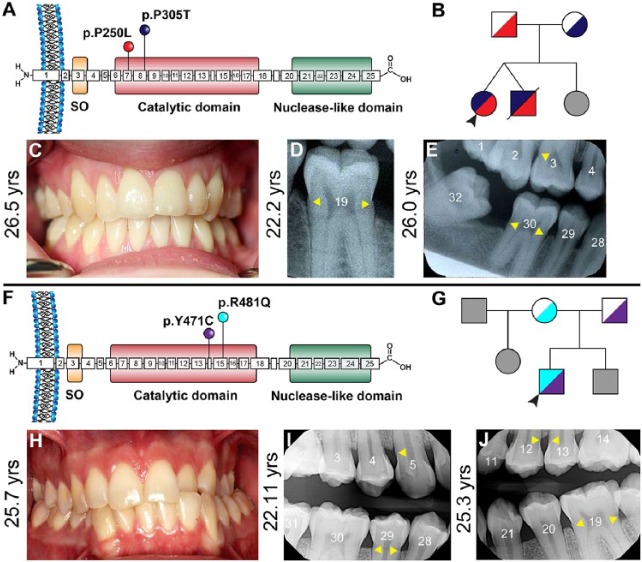
Figure 2.
Clinical presentations of generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI) in subjects 4 and 5. (A) Schematic of ENPP1 protein indicating locations of p.P250L (exon 7) and p.P305T (exon 8) amino acid substitutions, both within the catalytic domain, identified in GACI subject 4. (B) Pedigree of proband subject 4 (black arrowhead) showing unaffected parents, twin brother who died of GACI in infancy, and unaffected younger sister (unknown genetic composition indicated by gray shading). (C) Oral photograph at 26.5 y reveals a healthy dentition and absence of caries, with generalized gingival recession. Dental bitewing radiographs at (D) 22.2 y of age and (E) 26.0 y show consistent protruding cervical root morphology (yellow arrowheads) in molars. (F) Schematic of ENPP1 protein indicating locations of p.Y471C (exon 14) and p.R481Q (exon 15) amino acid substitutions, both within the catalytic domain, identified in GACI subject 5. (G) Pedigree of proband subject 5 (black arrowhead) showing unaffected parents and stepfather and unaffected brother and stepsister (unknown genetic composition indicated by gray shading). (H) Oral photograph at 25.7 y reveals a relatively healthy dentition with unilateral crossbite and localized areas of gingival recession. Mild gingival hyperplasia is noted between maxillary central incisors. Dental bitewing radiographs at (I) 22.11 and (J) 25.3 y show consistent protruding cervical root morphology (yellow arrowheads) in posterior teeth and slightly narrow root canals in incisors.