Fig. 2. STDP shifts towards LTP in guinea pigs with tinnitus.
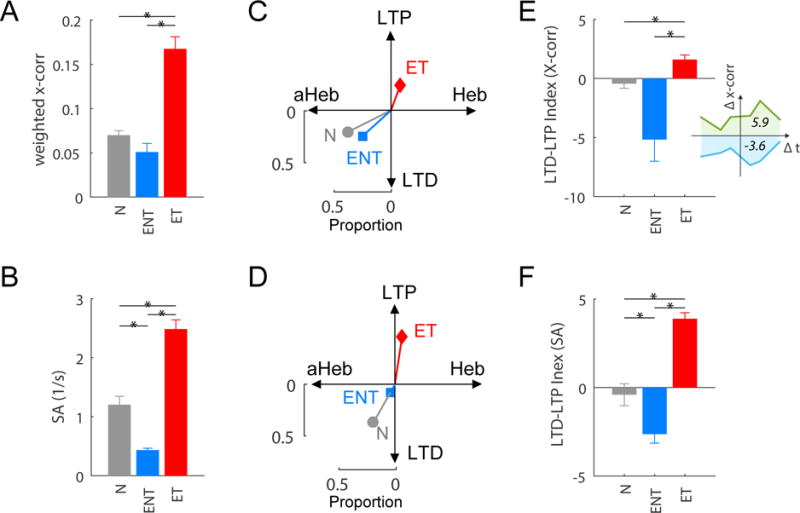
(A) Increased mean cross-correlation coefficient (x-corr; weighted by the proportion of synchronous unit-pairs) and (B) increased mean spontaneous activity (SA) compared to the normal-hearing (N) and exposed-but-no-tinnitus (ENT) groups of animals. * P< 0.05; data shown are mean ± SEM. Spontaneous activity for the N, ENT, and ET groups was 116, 93, 167 unit-pairs for x-corr, and 106, 387, 478 units, respectively. (C, D) A shift in the proportion of learning rules towards Hebbian-like (Heb; x-axis) and LTP (y-axis) in the ET group for (C) synchrony and (D) spontaneous activity (SA). (E, F) LTD-LTP index (total magnitude of LTP i.e. green area under curve relative to total magnitude of LTD i.e. blue area above curve of learning rules (E inset) is increased in the ET group for (E) synchrony and (F) spontaneous activity (SA).
