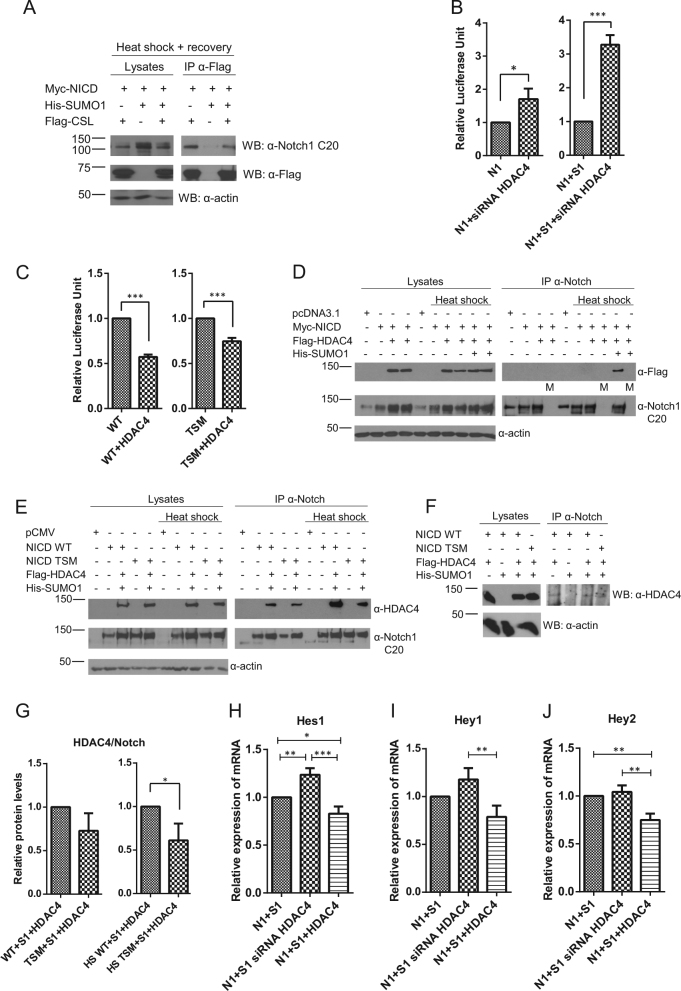
Fig. 7.
HDAC4 decreases Notch1 activity in the presence of SUMO. a Sumoylated Notch1 binds to CSL and remains bound to DNA. n = 4. b Blocking the expression of HDAC4 by siRNA increases Notch1 activity. Notch1 activity was measured from HeLa cells by the 12×CSL luciferase reporter reflecting the activity of the Notch1 signaling pathway. The values shown are normalized luciferase units. The difference in Notch1 activity is greater in samples with overexpressed SUMO1 (S1) n = 3. c HDAC4 represses the activity of wild-type GFP-Flag-NICD1 (WT) more than it represses the activity of the K1774/1780/1781/1782R GFP-Flag-NICD1 (TSM). n = 3. d SUMO increases Notch1–HDAC4 interaction. Control samples without antibody during IP are indicated with an “M” referring to mock. n = 3. e Consistent with the results in (c), K1774/1780/1781/1782R GFP-Flag-NICD1 (NICD TSM) decreases NICD1–HDAC4 interaction compared to wildtype NICD1 (NICD WT). f Notch interacts with HDAC4 on the DNA. n = 3. g The levels of HDAC4 as related to Notch in the immunoprecipitates in (e) were quantified. Values indicate the average of three independent experiments. n = 3. h–j Inhibition of HDAC4 expression by siRNA increases, and HDAC4 overexpression decreases the expression of Notch1 (N1) target genes Hes1, Hey1, and Hey2 in the presence of SUMO1 (S1). The relative expression of mRNA was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. n = 3