Fig. 6. The coral host modulates the endocytic pathway and enhances phagosome maturation and lysosome fusion in response to Chromera.
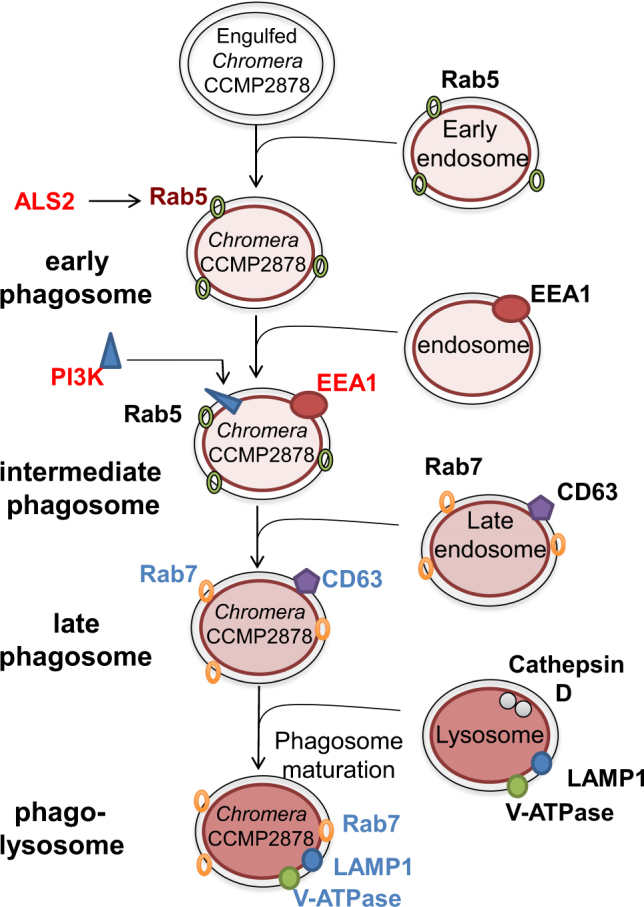
Upon phagocytosis, the phagosome acquires the GTPase Rab5 via fusion with early endosomes. The Rab5 effector ALS2 was also upregulated. Rab5 acts to recruit phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K), which generates phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P) and recruits early endosomal antigen (EEA1) from endosomes. EEA1 is a Rab5 effector protein and its upregulation triggers fusion of the phagosome with a late endosome. During the phagosome maturation process, Rab7 replaces Rab5 and the intermediate phagosome fuses with late endosomal vesicles, acquiring a suite of proteins that includes the proton-ATPase pump (V-ATPase), lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 1 (LAMP1), CD63, and lysosomal hydrolases. Vacuoles containing Chromera fuse with late endosomes/lysosomes as indicated by the upregulation of genes encoding Rab7, LAMP1, and CD63 (plus late endosomal/ lysosomal adapter, SNAP-associated protein and vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 (VAMP7) “not shown”). The observed upregulation of the lysosomal V-ATPase signals the formation of phagolysosomes, which are typically rich in hydrolytic enzymes and have an extremely low pH, presumably in order to eliminate Chromera. Genes in red text are downregulated, while those in blue are upregulated
