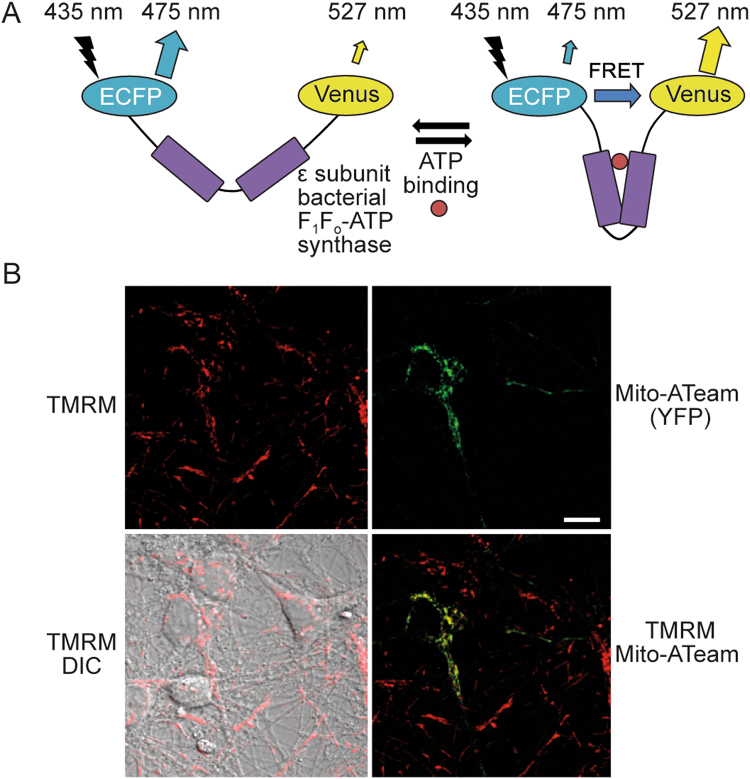
Fig. 5. mitoATeam, a FRET-based reporter of mitochondrial ATP, can be transfected into primary neurons.
[99] a The reporter comprises a linker protein (ε-subunit of a bacterial F1Fo ATP synthase) inserted between a donor CFP and acceptor YFP (enhanced CFP and Venus). ATP binding induces a conformational change in the linker protein, increasing FRET between the two FPs and altering the emitted fluorescence. Ratiometric measurements are obtained by calculating the FRET ratio (CFP/YFP). The acceptor YFP can also be laser-excited at ~488 nm. Fluorescent emissions from both FPs should be monitored, to ensure that any ratio change is due to altered FRET (opposite changes in the fluorescence of the individual FPs), rather than other sources (such as increased auto-fluorescence). Image reproduced with permission from [12]. b Representative images of primary mouse cortical neurons (DIV8) transfected with mitoATeam, stained with TMRM, and imaged on a Zeiss LSM 710 confocal microscope. Mitochondrial localisation of the mitoATeam probe was verified by colocalisation with the TMRM signal (merged TMRM and Mito-ATeam image). Scale bar = 10 μm. DIC differential interference contrast