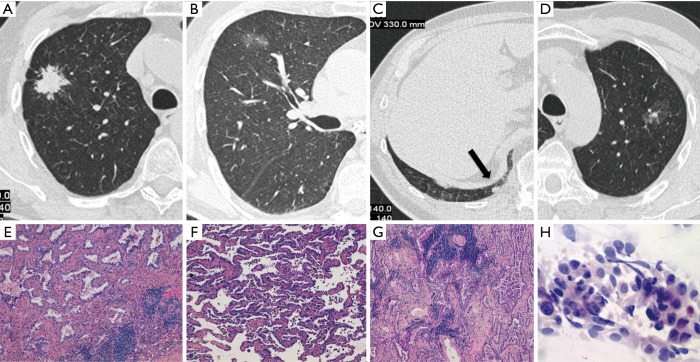
Figure 1.
Case I (Table 1). Four primary adenocarcinomas in a 70-year-old smoker, which were all detected at baseline LDCT screening round. They appeared as a spiculated lung nodule in the right upper lobe (RUL) (A), a ground glass opacity in the same lobe (B), a small solid nodule in the right lower lobe (RLL) (arrow in C) and a ground glass opacity with a small solid component in the left upper lobe (LUL) (D). Haematoxylin and eosin histologic staining (original magnification ×200) demonstrate an invasive adenocarcinoma, acinar predominant (E) in the RUL lesion corresponding to (A), an invasive adenocarcinoma, lepidic predominant (F) in the RUL lesion corresponding to (B) and an invasive adenocarcinoma, acinar predominant (G) in the RLL lesion corresponding to (C). Papanicolaou stain (original magnification ×40) of fine needle aspiration biopsy shows papillary pattern of uniform malignant cells with irregular nuclei consistent with adenocarcinoma (H) in the LUL lesion corresponding to (D).