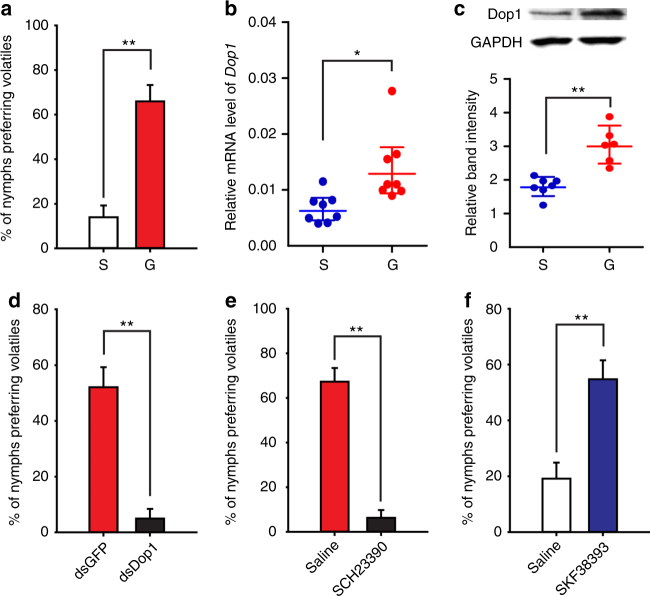
Fig. 1.
Dop1 regulates the olfactory attraction to gregarious volatiles in the migratory locust. a Gregarious locusts showed higher olfactory preference for gregarious volatiles than solitarious locusts (n = 44 and 41, G-test). b, c Dop1 mRNA (b, n = 8) and protein levels (c, n = 6) significantly differed in the brains of solitarious and gregarious locusts (Student’s t-test). d Dop1 RNAi knockdown reduced the olfactory response of gregarious locusts to their volatiles (n = 48 and 40). e Injection of the Dop1 antagonist SCH23390 reduced the olfactory response of gregarious locusts to their volatiles (n = 54 and 48). f Injection of the Dop1 agonist SKF38393 enhanced the olfactory preference of solitarious locusts to gregarious volatiles (n = 47 and 41). The asterisks outside the strip indicate the significant difference between controls and the treatments through G-test for independence (d, e, f). The data in b and c are shown as mean ± SEM and the data in a, d, e, and f are shown as proportion (p) ± SE *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. S: solitarious, G: gregarious