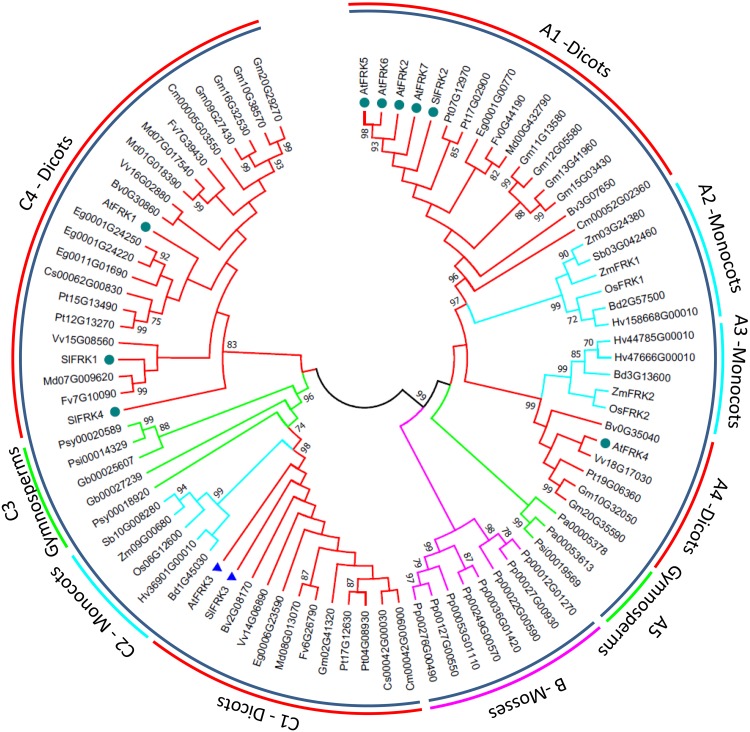
FIGURE 3.
Phylogenetic tree of FRK genes from land plants. Amino acid sequences were retrieved using the Plaza 3.0 tool for gene family analysis (Van Bel et al., 2017). Partial sequences and sequences identified as FRK-like (FLNs) based on their length and insertions were excluded, leaving a total of 88 sequences. Confirmed FRK genes were renamed based on previous annotations. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW with default options and analyzed in MEGA 7.0 (Kumar et al., 2016). The tree was created using the maximum-likelihood method based on the JTT matrix-based model (Jones et al., 1992). Bootstrap values >70% are denoted at the nodes. The pink branches belong to the mosses. Green branches belong to in the gymnosperms. Turquoise branches belong to the monocots and red branches belong to the dicots. Dark green circles indicate FRKs that were confirmed to be cytosolic and blue triangles indicate FRKs that were confirmed to be plastidic.