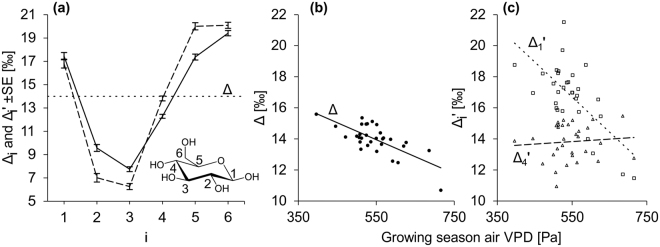
Figure 1.
Intramolecular 13C distributions and effects of growing season air vapour pressure deficit (VPD) on 13C discrimination. Data were acquired for tree-ring glucose of Pinus nigra laid down from 1961 to 1995 at a site in the Vienna basin. (a) Intramolecular 13C distributions (means over 31 years) expressed in terms of intramolecular 13C discrimination. Solid line, observed distribution (Δi); dashed line, TPC-free distribution (Δi′); dotted line, hypothetical distribution without positional 13C effects. Insert: Glucose unit of cellulose showing intramolecular locations of carbon positions, i. (b,c) Effects of VPD on whole-molecule 13C discrimination, Δ and on positional 13C discrimination at C-1 and C-4; Δ1′ and Δ4′, respectively. Linear regression demonstrates highly significant negative relationships between VPD and both Δ and Δ1′, and no detectable relationship between VPD and Δ4′ (ordinary least squares regressions, n = 31, Δ = −0.011VPD + 20.0, r = −0.72, p = 5.4*10−6; Δ1′ = −0.023VPD + 29.1, r = −0.68, p = 3*10−5; Δ4′ = 0.002VPD + 12.9, r = 0.09, p = 0.64).