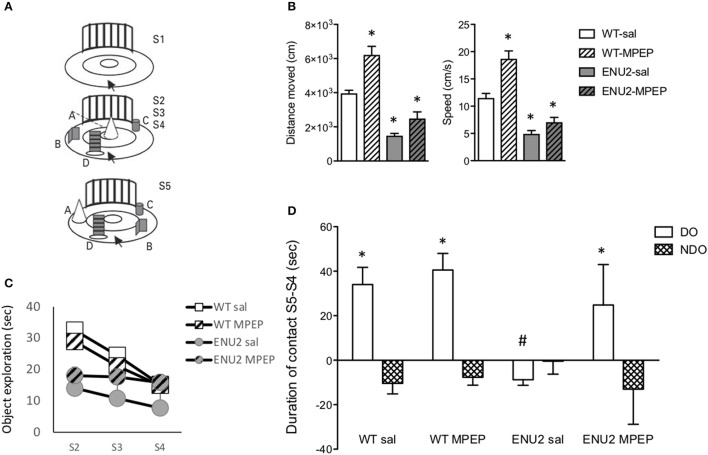
Figure 6.
Pharmacological blockade of mGlu5 receptors improves cognitive performances in the spatial novelty test in ENU2 mice. The same open field arena (A) was used for the sequential assessment of locomotor activity (S1), object exploration (S2–S4), and spatial novelty (S5) in WT and ENU2 mice treated i.p. with either saline or MPEP (20 mg/kg). For the whole behavioral analysis we used 12 WT mice treated with saline, 7 WT mice treated with MPEP, 5 ENU2 mice treated with saline, and 5 ENU2 mice treated with MPEP. Values are always expressed as means ± S.E.M. Locomotor activity is expressed as distance moved and speed in (B,C), respectively, where *p < 0.05 vs. the respective values obtained in WT mice treated with saline (Two-way ANOVA + Fisher's LSD); genotype x treatment: (B) [F(1, 24) = 6.15; p = 0.02; (C) F(1, 25) = 4.95; p = 0.03]. Statistical analysis in (D) was performed by Three-way ANOVA + Fisher's LSD. Test × treatment: [F(1, 32) = 4.37; p = 0.04]. Post-hoc: p < 0.05 vs. the respective NDO-values (*) or vs. all other DO-values (#). DO, Displaced Objects; NDO, Non Displaced Objects.